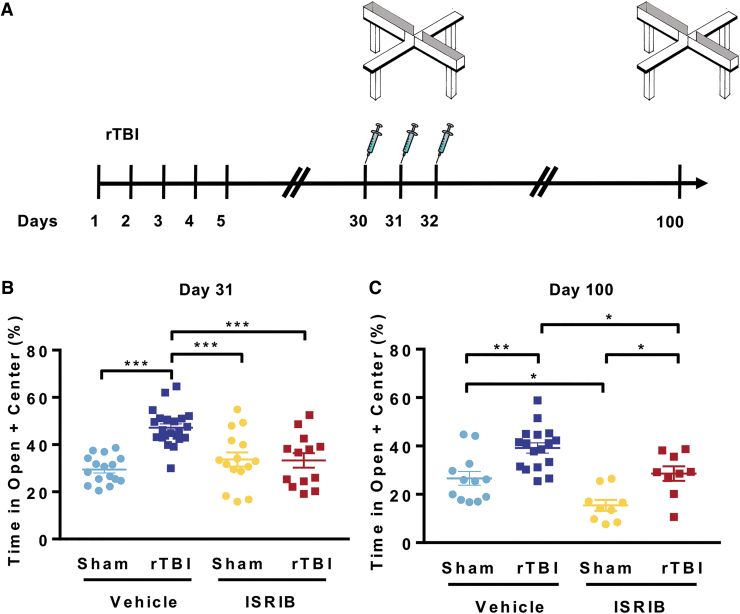
FIG. 3.
Small molecule integrated stress response inhibitor, ISRIB, reverses repetitive traumatic brain injury (rTBI) mediated risk-taking behavior. (A) Experimental Design. Elevated Plus maze was performed at ∼31 and 100 days post-injury (dpi). The ISRIB (2.5 mg/kg intraperitoneal) was administered on days 30, 31, and 32 dpi. (B) A single ISRIB dose (2.5 mg/kg intraperitoneal) reversed trauma-induced risk-taking behavior at one month post-surgery. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) measures significant injury (p < 0.001), ISRIB (p < 0.05), and ISRIB x injury effect (p < 0.001). Tukey post hoc analysis revealed differences between groups. (C) Permanent changes in risk-taking behavior were observed at ∼3 months (100 days) post-injury. Three injections of ISRIB (70 days prior) completely reversed trauma-induced behavioral changes. Two-way ANOVA measures significant injury (p < 0.001) and ISRIB (p < 0.001) effect. Tukey post hoc analysis revealed differences between groups. Individual animal scores represented in dots; lines depict group mean and standard error of the mean. Color image is available online.