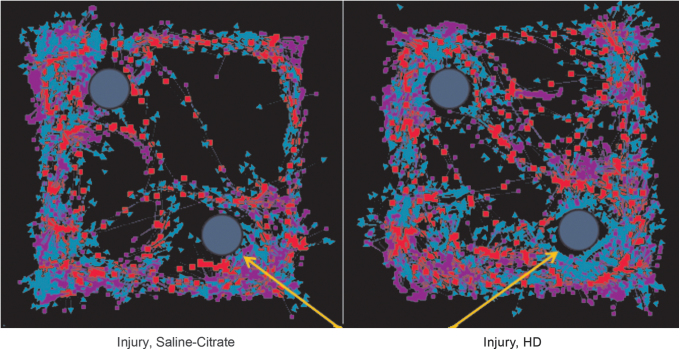
FIG. 6. .
Mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) alters object exploration in the Novel Object Recognition Test. This figure shows a representative EthoVision tracing of the Novel Object Recognition test quantified in Figure 7. The yellow arrows represent the novel object. Blue arrows in the tracking represent nose-point tracking, whereas red squares indicate body center tracking and purple squares indicate tail base tracking. The injured animal, treated with vehicle (left) spent similar time at both objects, hence an inability to discriminate between novel and familiar objects. The animal receiving a chronic high dose of cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeONPs) showed preferential investigation of the novel object, indicative of improved memory.