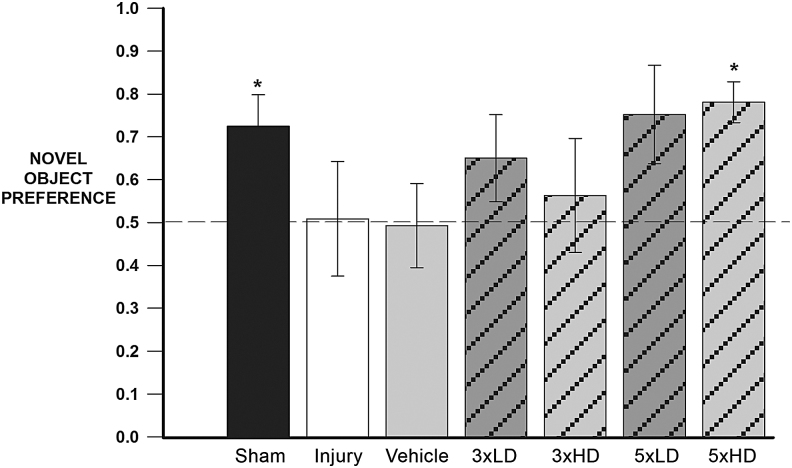
FIG. 7.
Chronic cerium oxide nanoparticle (CeONP) administration after mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) improves performance in the Novel Object Recognition (NOR) Test. This graph depicts the novel object preferences for each treatment group. The dotted line represents the novel object preference score of an animal unable to discern between novel and familiar objects (indicative of memory deficit). Intact memory was observed in the sham and chronic high dose group, as the novel object recognition value was significantly higher than 0.5 (p = 0.0383 and p = 0.0041, respectively). Injury-induced memory deficits resulted in novel object preferences not significantly different from 0.5. The chronic low dose treatment group showed trending differences in memory improvement (score >0.5) with p = 0.0794. The chronic high dose animals showed significant improvement in NOR scores, which were similar to those of controls. Data are expressed as μ+SE. *Significant from 0.5, p < 0.5.