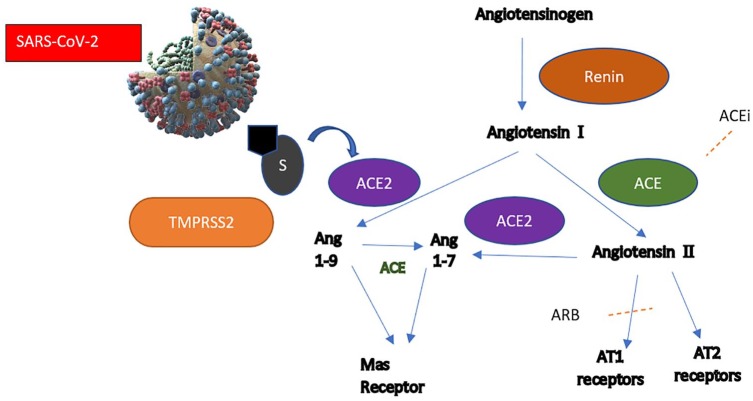
Figure 1.
Traditional RAAS pathway, presumed ACE2 pathway and sites of ACEi and ARB action are highlighted. The ACE2 pathway is thought to increase vasodilatory peptides (Ang 1–9, Ang 1–7) and decrease downstream effects of RAAS activation. ACEi might upregulate ACE2 expression. The effect of ARB use is probably slightly different from ACEi, as angiotensin II and ACE levels remain unaffected. Viral entry is thought to be via ACE2 receptor in the presence of transmembrane serine protease.
RAAS: renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system; ACE: angiotensin-converting enzyme; AT1: angiotensin receptor type 1; AT2: angiotensin receptor type 2; ARB: angiotensin receptor blocker; ang: angiotensin; S: spike protein; Mas receptor: Mitochondrial assembly receptor.