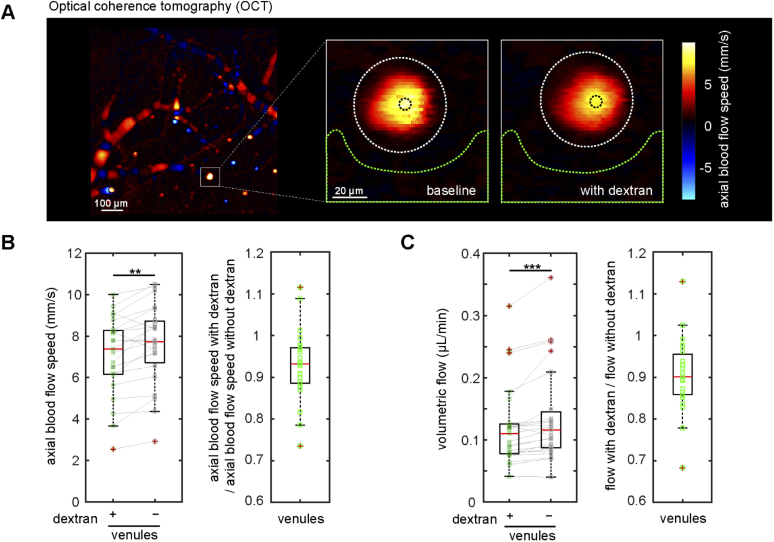
Fig. 4.
Doppler optical coherence tomography confirmed that intravascular high molecular weight dextran slows blood flow in cortical ascending venules. (A) Doppler OCT image of the cortical surface (left, scale bar is 100 µm), and zoomed-in views of the ascending venule indicated by the white square taken at baseline and shortly after intravascular injection of high molecular weight dextran (right, scale bar is 20 µm). Colors correspond to axial blood flow speeds, as indicated with the color bar. (B) Axial blood flow speed from ascending venules at baseline and after dextran injection (left). Measurements from same venule are connected with a solid line. Ratio of axial flow speed with and without dextran (right) (23 venules from 3 mice). (C) Volumetric blood flow with and without dextran (left) and the corresponding ratio (right). ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Data were normally distributed for flow speed (panel B) so a paired t-test was used. Data were not normally distributed for volumetric flow (panel C) so Wilcoxon tests were used.