Fig. 2.
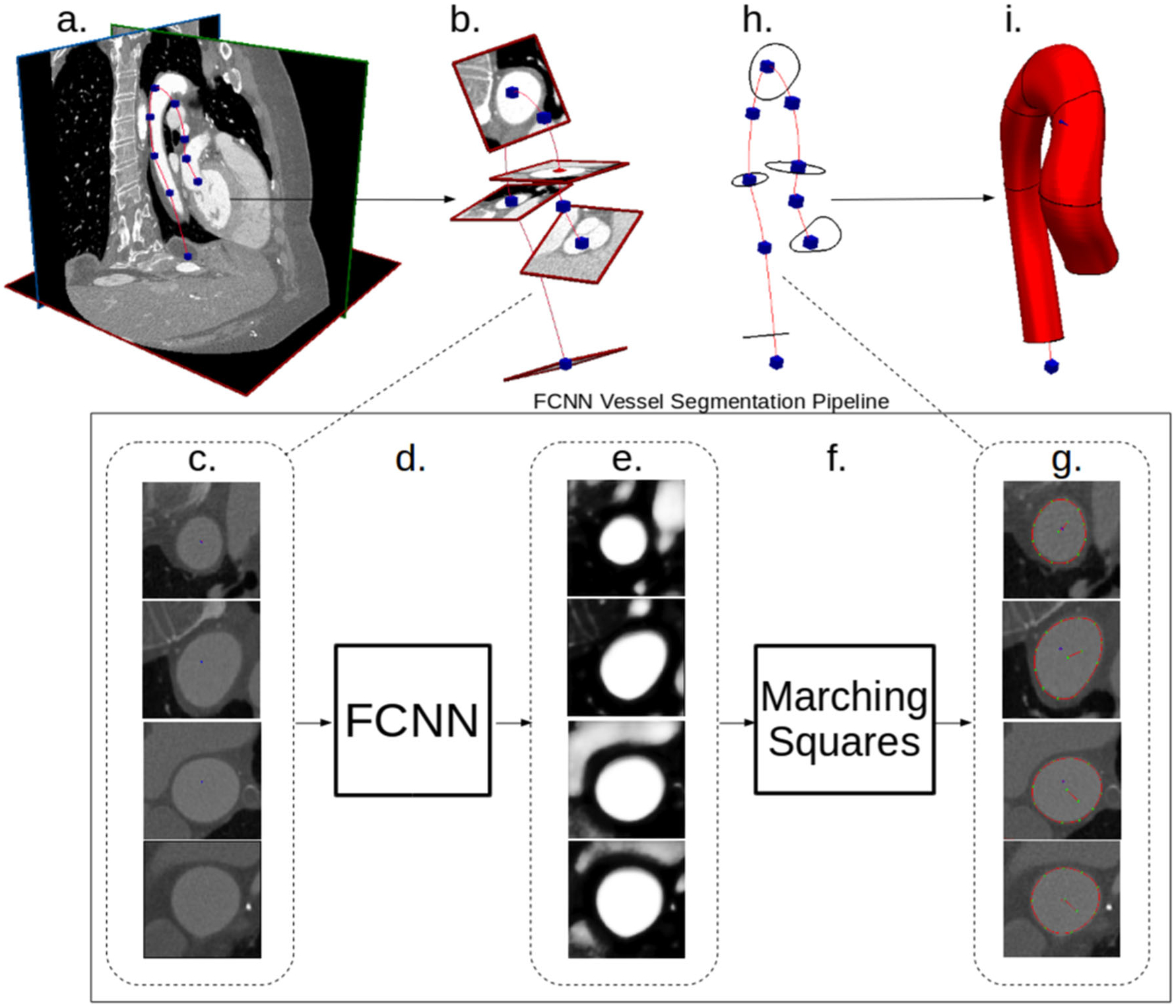
Our proposed FCNN-based cardiovascular model building pipeline. a Image data and vessel pathline supplied by the user. b Path information is used to extract image pixel intensities in plane perpendicular to the vessel path. c 2D images extracted along vessel pathlines are input to the FCNN. d FCNN acts on the input images to compute local vessel enhancement images. e Vessel enhancement images computed by the FCNN, the pixel values are between 0 and 1 indicating vessel tissue likelihood. f The marching-squares algorithm is applied to each enhanced image to extract the central vessel segmentation. g 2D extracted vessel surface points overlayed on original input images. h The 2D vessel surface points are transformed back to 3D space. i 3D cross-sectional vessel surfaces are interpolated along the pathline to form the final vessel model
