Figure 3. Genetic Characterization of ASD Genes.
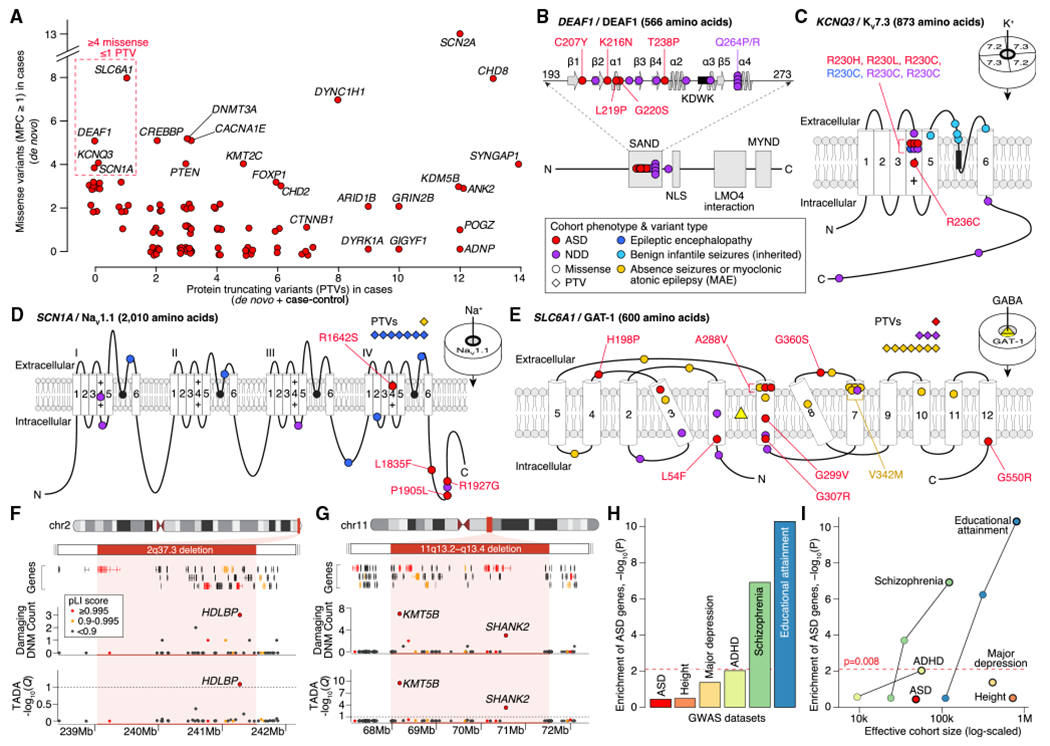
(A) Count of PTVs versus missensevariants(MPC ≥ 1) in cases for each ASD-associated gene (red points, selected genes labeled). These counts reflect the data used by TADA for association analysis: de novo and case-control data for PTVs; de novo only for missense.
(B) Location of ASD de novo missense variants in DEAF1. The five ASD variants (marked in red) are in the SAND (Sp100, AIRE-1, NucP41/75, DEAF-1) DNA-binding domain (amino acids 193–273, spirals show α helices, arrows show β sheets, KDWK isthe DNA-binding motif) alongside 10 variants observed in NDD, several of which have been shown to reduce DNA binding, including Q264P and Q264R (Chen et al., 2017; Heyne et al., 2018; Vultovan Silfhout et al., 2014).
(C) Location of ASD missensevariants in KCNQ3. All four ASD variants are located in the voltage sensor (fourth of six transmembrane domains), with three in the same residue (R230), including the gain-of-function R230C mutation observed in NDD (Heyne et al., 2018; Miceli et al, 2015). Five inherited variants observed in benign infantile seizures are shown in the pore loop (Landrum et al., 2014; Maljevic et al., 2016).
(D) Location of ASD missense variants in SCN1A along side 17 de novo variants in NDD and epilepsy (Heyne et al., 2018).
(E) Location of ASD missense variants in SLC6A1 along side 31 de novo variants in NDD and epilepsy (Heyne et al., 2018; Johannesen et al., 2018).
(F) Subtelomeric 2q37 deletions are associated with facial dysmorphisms, brachydactyly, high BMI, NDD, and ASD (Leroy et al., 2013). Although three genes within the locus have a pLI score of 0.995 or higher, only HDLBP is associated with ASD.
(G) Deletions atthe 11q13.2–q13.4 locus have been observed in NDD, ASD, and otodental dysplasia (Coe et al., 2014; Cooperet al., 2011). Five genes within the locus have a pLI score of 0.995 or higher, including two ASD genes: KMT5B and SHANK2.
(H) Assessment of gene-based enrichment, via MAGMA, of 102 ASD genes against genome-wide significant common variants from six GWASs.
(I) Gene-based enrichment of 102 ASD genes in multiple GWASs as a function of effective cohort size. The GWAS used for each disorder in (I) has a black outline.
Statistical tests: (F) and (G), TADA; (H) and (I), MAGMA.
