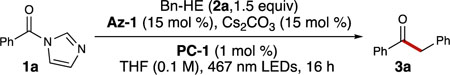
Table 1.
Optimization of reaction conditionsa
 | ||
|---|---|---|
| entry | deviation from standard | GC yield (%)a,b |
| 1 | none | 63 |
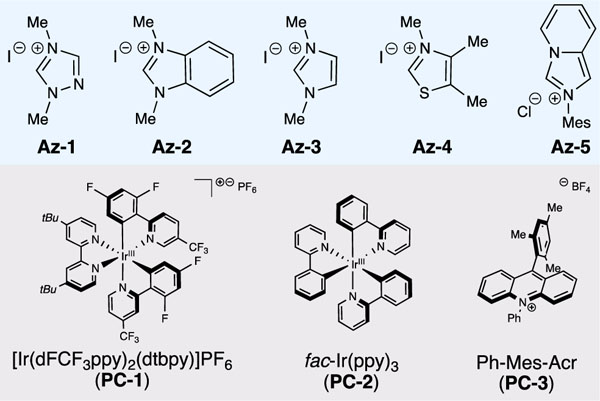
| 2 | PC-2 instead of PC-1 | 11 |
| 3 | PC-3 instead of PC-1 | 0 |
| 4 | Az-2 instead of Az-1 | 14 |
| 5 | Az-3 instead of Az-1 | 0 |
| 6 | Az-4 instead of Az-1 | 0 |
| 7 | Az-5 instead of Az-1 | 11 |
| 8 | CsOAc instead of Cs2CO3 | 38 |
| 9 | K2CO3 instead of Cs2CO3 | 8 |
| 10 | Li2CO3 instead of Cs2CO3 | 0 |
| 11 | CH3CN instead of THF | 72 |
| 12 | CH2CI2 instead of THF | 41 |
| 13 | DMF instead of THF | 65 |
| 14 | no light | 0 |
| 15 | no photocatalyst | 0 |
| 16 | no Az | 0 |
| 17 | no base | 0 |
 | ||
Gas chromatography (GC) yield is based on a calibration curve using 1,3,5-trimethoxybenzene as the internal standard.
Reaction conditions: 1a (0.10 mmol), Bn–HE 2a (0.15 mmol), Az (0.015 mmol), base (0.015 mmol), PC (1 μmol), solvent (0.1 M; THF, tetrahydrofuran; DMF, dimethyformamide) for 16 h.
