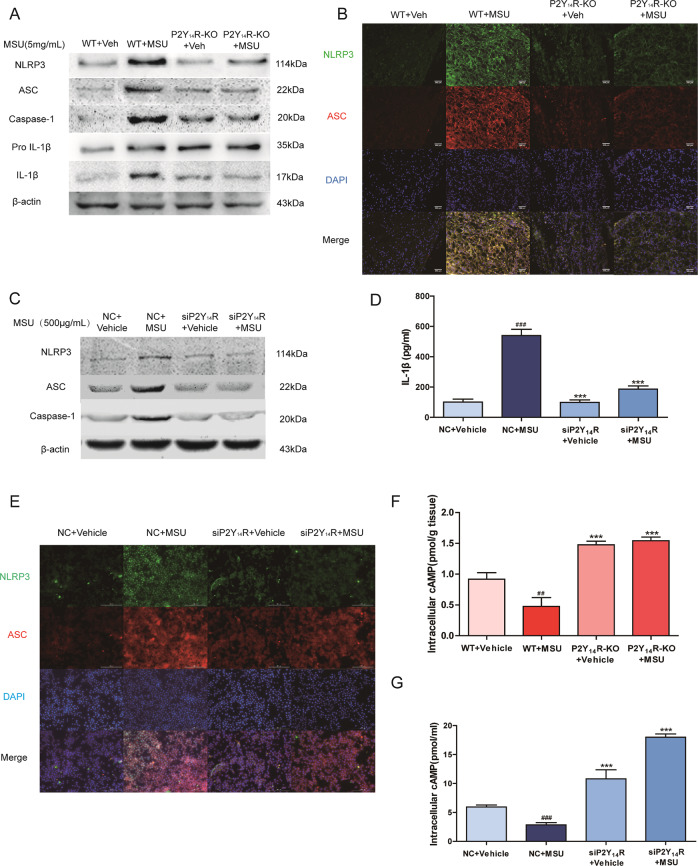
Fig. 2. NLRP3 inflammasome activation was involved in P2Y14R deficiency.
a The NLRP3 inflammasome activation and IL-1β mutation in synovium was inhibited in P2Y14R-KO rats detected by western blotting. The relative optical density was exhibited in the supplementary materials (n = 4). b Immunofluorescence assay confirmed that MSU-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in synovial tissue of WT but not P2Y14R-KO rats. NLRP3 protein was marked with Alexa Fluor 488 (Green). ASC protein was marked with Alexa Fluor 647 (Red). DAPI (Blue) was used to mark the nucleus. c The expression of NLRP3 inflammasome activation was inhibited under P2Y14R knockdown. P2Y14R siRNA was used to transfect THP-1 cells for 48 h, followed by MSU stimulation for 12 h. The relative optical density was exhibited in the supplementary materials (n = 4). d ELISA kit data showed that the release of IL-1β decreased when P2Y14R was knockdown with siRNA. e Immunofluorescence assay revealed that MSU administration could not induce the NLRP3 inflammasome activation anymore in siP2Y14R THP-1 cells. NLRP3 protein was marked with Alexa Fluor 488 (Green). ASC protein was marked with Alexa Fluor 647 (Red). DAPI (Blue) was used to mark the nucleus. f The intracellular cAMP level in synovial tissue increased in P2Y14R-KO rats compared WT ones (n = 6). g The intracellular cAMP level in THP-1 cells increased under P2Y14R knockdown (n = 4). The data were presented as means ± SDs. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Tukey multiple comparison test was performed. Compared with WT/NC + vehicle group: #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001. Compared with WT/NC + MSU group: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (n = 4).