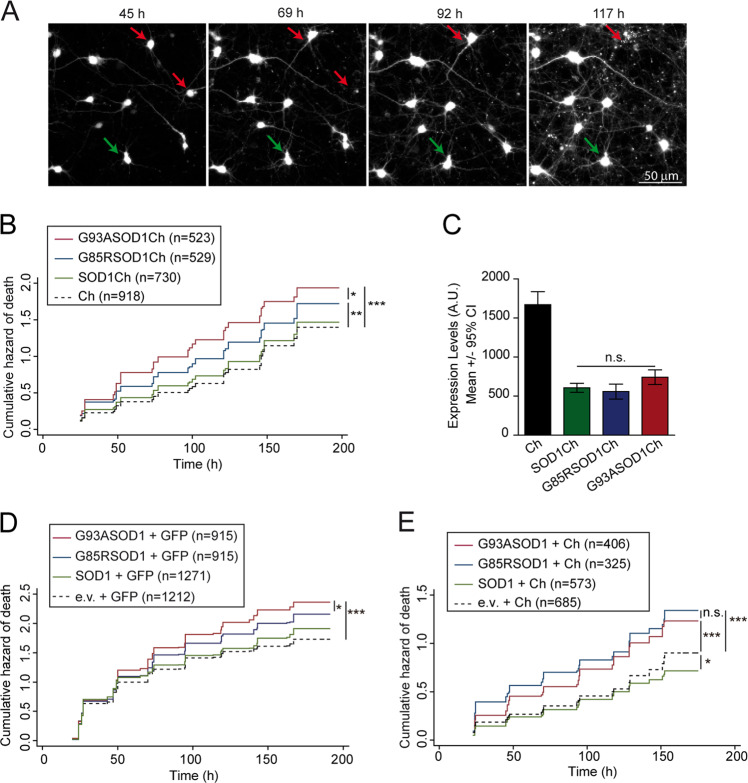
Fig. 1. Pathological SOD1 mutants G93A and G85R increase significantly the risk of neuronal death in rat cortical primary neurons.
a Example of longitudinal tracking of individual primary cortical neurons expressing monomeric Cherry (Ch) with automated microscopy. Red arrows indicate neurons that die over the course of the experiment. Green arrows point to a neuron tracked longitudinally that survive up to 117 h. b Cumulative hazard estimates of primary neurons transfected with WT and pathological versions of SOD1 (SOD1Ch, G85RSOD1Ch, G93ASOD1Ch) and Ch as control. Cox proportional hazard (CPH) analysis; pooled data from three independent experiments. c Ch fluorescence intensity of individual neurons 20–24 h after transfection (Kruskal–Wallis and Dunn’s post hoc test, Ch = 66, SOD1Ch = 60, G85RSOD1Ch024 and G93ASOD1Ch = 54 neurons from a representative experiment). d Cumulative hazard estimates of primary neurons co-transfected with GFP and SOD1 versions (WT and pathological mutants G85R and G93A). CPH analysis; pooled data from four independent experiments. e Cumulative hazard estimates of primary neurons co-transfected with Ch and SOD1 versions. CPH analysis, pooled data from two independent experiments. Number of neurons (n), all error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals (CIs), non-significant (n.s.), *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001.