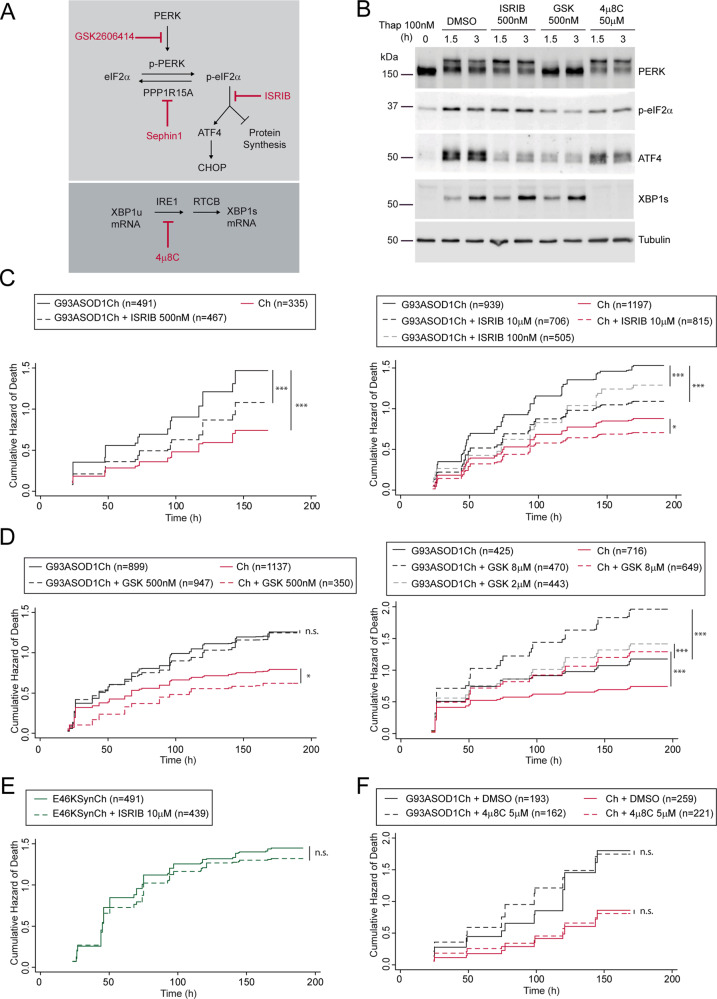
Fig. 3. ISRIB decreases G93A SOD1-dependent neuronal death.
a Scheme depicting the modes of action of GSK2606414 (GSK), ISRIB, Sephin1, and 4μ8C in PERK and IRE1-dependent signaling. XBP1u (unspliced XBP1), XBP1s (spliced XBP1), and RTCB (RNA ligase enzyme that joins the exons resulting from XBP1 intron removal by IRE1). b Western blot analysis of PERK, p-eIF2α, ATF4, XBP1s, and tubulin (loading control) from HEK293 protein extracts treated with 100 nM thapsigargin (Thap) and 500 nM ISRIB, 500 nM GSK, 50 μM 4μ8C, and DMSO as control. Representative experiment from at least n = 3. c Cumulative hazard estimates of primary neurons transfected with SOD1 pathological version G93ASOD1Ch and treated with 500 nM, 100 nM, and 10 μM ISRIB (Ch as control). CPH analysis; pooled data from three independent experiments (left panel) and five independent experiments (right panel). d Cumulative hazard estimates of primary neurons transfected with G93ASOD1Ch and treated with 500 nM, and 2 and 8 μM GSK (Ch as control). CPH analysis; pooled data from three independent experiments (left panel) and two independent experiments (right panel). e Cumulative hazard estimates of primary neurons transfected with aSyn pathological version (E46KSynCh) and treated with 10 μM ISRIB. CPH analysis; pooled data from three independent experiments. f Cumulative hazard estimates of primary neurons transfected with G93ASOD1Ch and treated with 5 μM 4μ8C (Ch as control). CPH analysis; representative experiment from two independent experiments. Number of neurons (n), non-significant (n.s.), *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001.