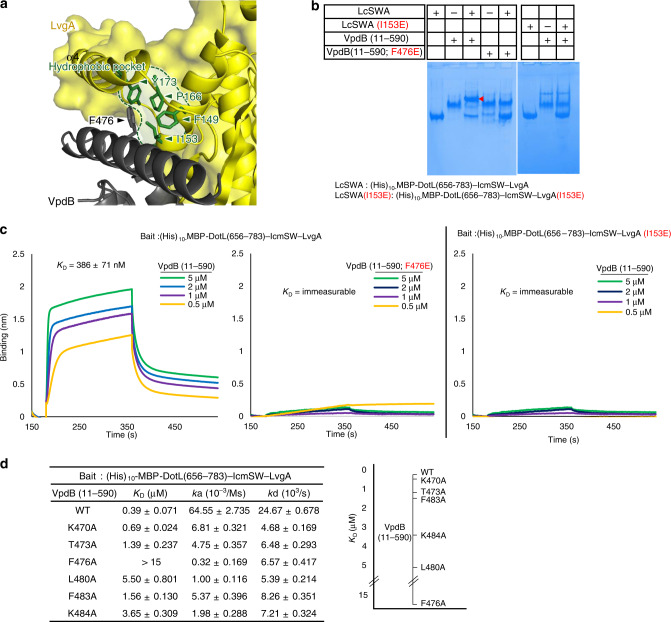
Fig. 2. Interaction between α1 of VpdB(461-590) and the LvgA subunit.
a A prominent hydrophobic interaction. Phe476 of VpdB packs against a hydrophobic pocket on LvgA indicated by the dotted line. Four residues that constitute the hydrophobic pocket are shown as sticks. b Native PAGE analysis. The VpdB(F476E) or LvgA(I153E) mutation disrupted the interaction between VpdB(11-590) and (His)10-MBP-DotL(656-783)–IcmSW–LvgA. c Quantification. The binding affinity between (His)10-MBP-DotL(656-783)–IcmSW–LvgA and VpdB(11-590) was drastically decreased by either VpdB(F476E) or LvgA(I153E) mutation. The interaction was measured by bio-layer interferometry, where the indicated bait was immobilized on a Ni-NTA biosensor via the N-terminal (His)10-MBP tag fused to DotL(656-783). The measurement was triplicated. d Alanine mutagenesis. Binding affinities between (His)10-MBP-DotL(656-783)–IcmSW–LvgA and VpdB(11-590) variants containing the indicated alanine substitution were analyzed by bio-layer interferometry. A plot of the measured KD values is shown on the right. Quantification was duplicated for each variant.