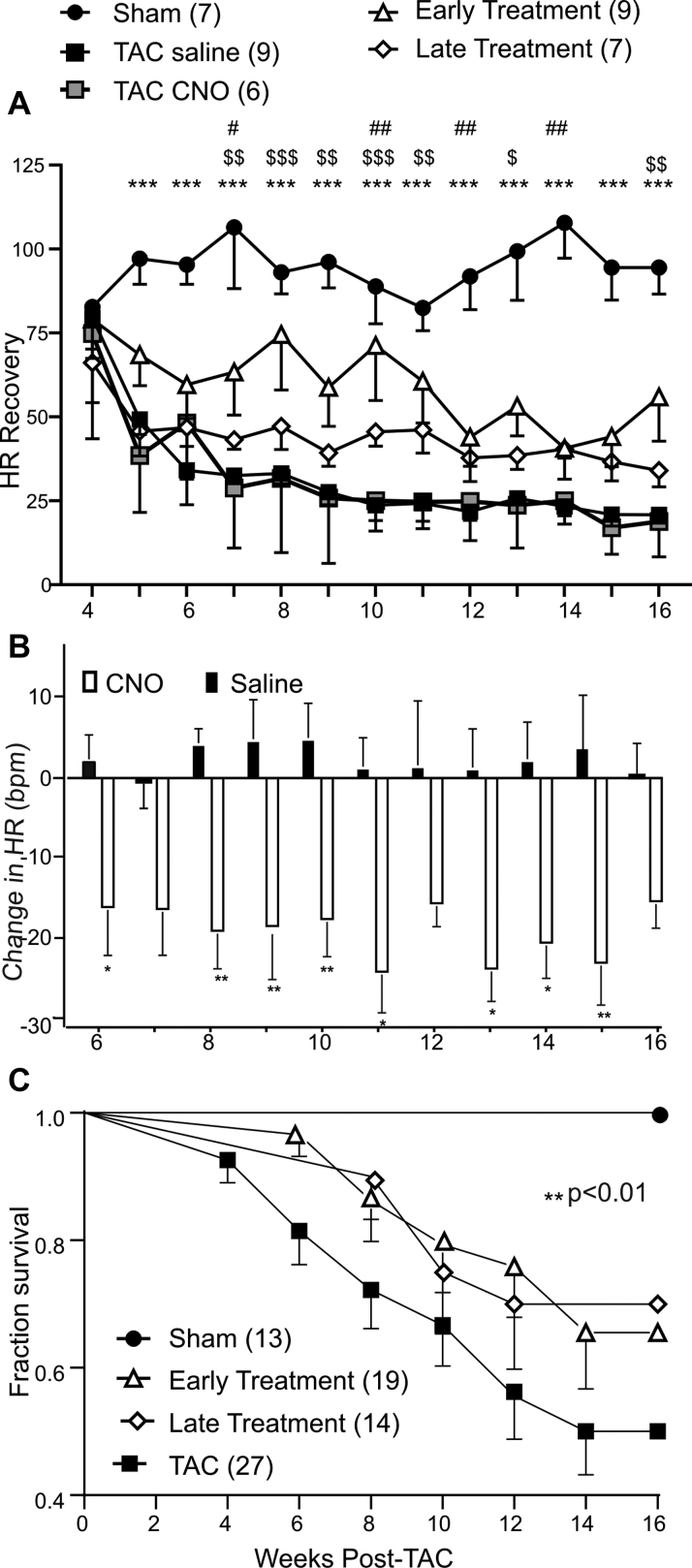
Figure 3.
Long-Term Activation of PVN Oxytocin Neurons Improves Heart Rate Recovery and Survival Rates in Animals With Heart Failure
(A) Longitudinal weekly measurements of heart rate recovery at 20-s post-treadmill stress test in Sham, TAC saline (expressing DREADDs), TAC CNO (not expressing DREADDs), and early-, and late-treatment animals from 4 to 16 weeks post-Sham/TAC surgery. All groups of animals expressing DREADDs in PVN oxytocin neurons were implanted with DSI ETA-F10 telemetry devices at 2 weeks post-TAC to measure electrocardiography and heart rate. Excitatory DREADDs activation was achieved by intraperitoneal injections of CNO (1 mg/kg) starting at 4 weeks post-TAC in the early-treatment group and 6 weeks post-TAC in the late-treatment group until 16 weeks post-TAC; Sham and TAC saline animals received saline injections. Heart rate recovery (HRR) was calculated as the heart rate at peak exercise minus 20-s recovery postexercise. TAC animals displayed significantly lower HRR from 5 to 16 weeks post-TAC compared with Sham animals. Early treatment significantly improved HRR at 7 to 11 and 16 weeks post-TAC compared with TAC animals. Data were analyzed using mixed-effects model with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test. Sham (n = 7); TAC (n = 9); early treatment (n = 9); late treatment (n = 7); TAC CNO (n = 6). ∗Sham vs. TAC; $TAC vs. early treatment; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p <0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. (B) Graph depicting changes in heart rate (beats per minute) in response to intraperitoneal injections of saline in TAC animals and CNO (1 mg/kg) in treatment animals from 6 to 16 weeks post-TAC/Sham. A significant reduction in heart rate was seen in all treatment animals at all weeks compared with saline-treated animals. Numbers in parentheses represent number of animals. Data were analyzed using mixed-effects model with Tukey’s multiple comparison post-test; ∗p < 0.05. (C) Kaplan-Meier curves depicting percent survival in Sham, combined TAC saline (expressing DREADDs), and TAC CNO (not expressing DREADDs), early- and late-treatment animals. TAC animals had significantly reduced survival compared with Sham, whereas early and late treatment significantly improved survival rates in animals with heart failure. Data were analyzed using log-rank test of survival analysis; overall significance is represented as ∗∗p < 0.01. CNO = clozapine-N-oxide; DREADDs = designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drug; PVN = paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus; TAC = transascending aortic constriction.