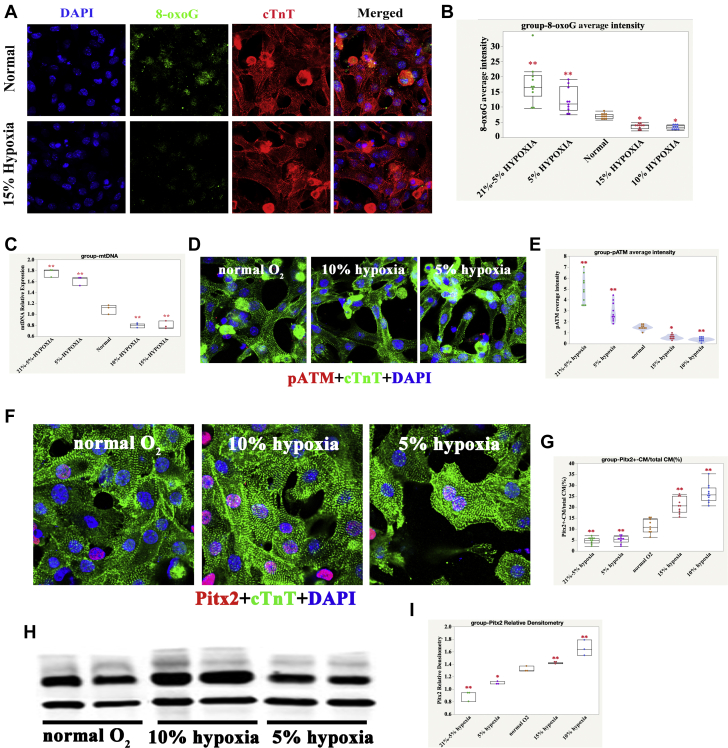
Figure 4.
Oxidative DNA Damage Was Significantly Reduced in 10% and 15% O2-Treated Human iPSC-CMs
(A) 8-oxoG in normal and 15% O2-Treated Human iPSC-CMs; cTnT (red), 8-oxoG (green), and DAPI (blue) stainings are shown. (B) Quantification of 8-oxoG IF intensity in differently O2-treated human iPSC-CMs; 1-way ANOVA, SNK; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, n = 10 fields from 3 independent experiments, compared with normal. (C) Quantification of mtDNA content in differently O2-treated human iPSC-CMs; 1-way ANOVA, SNK; ∗∗p < 0.01, n = 3 replicates compared with normal. (D) pATM in normal, 10%, and 5% O2-treated human iPSC-CMs; cTnT (green), pATM (red), and DAPI (blue) stainings are shown. (E) Quantification of pATM IF intensity in differently O2-treated human iPSC-CMs; 1-way ANOVA, SNK; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01, n = 10 fields from 3 independent experiments compared with normal. (F) IF graph of Pitx2 in normal, 10% hypoxia, and 5% hypoxia iPSC-CMs; cTnT (green), Pitx2 (red), and DAPI (blue) staining are shown. (G) Quantification of Pitx2 positive CMs in normal, 10% hypoxia, and 5% hypoxia iPSC-CMs. One-way ANOVA, SNK, n = 10 fields from 3 independent experiments; ∗∗p < 0.01, compared with group B (moderate hypoxia). (H) Western blot graph of Pitx2 in normal, 10% hypoxia, and 5% hypoxia iPSC-CMs. (I) Quantification of Pitx2 densitometry in normal, 10% hypoxia, and 5% hypoxia iPSC-CMs. One-way ANOVA, SNK, n = 3 samples; ∗∗p < 0.01, compared with group B (moderate hypoxia). Abbreviations as Figures 1, 2, and 3.