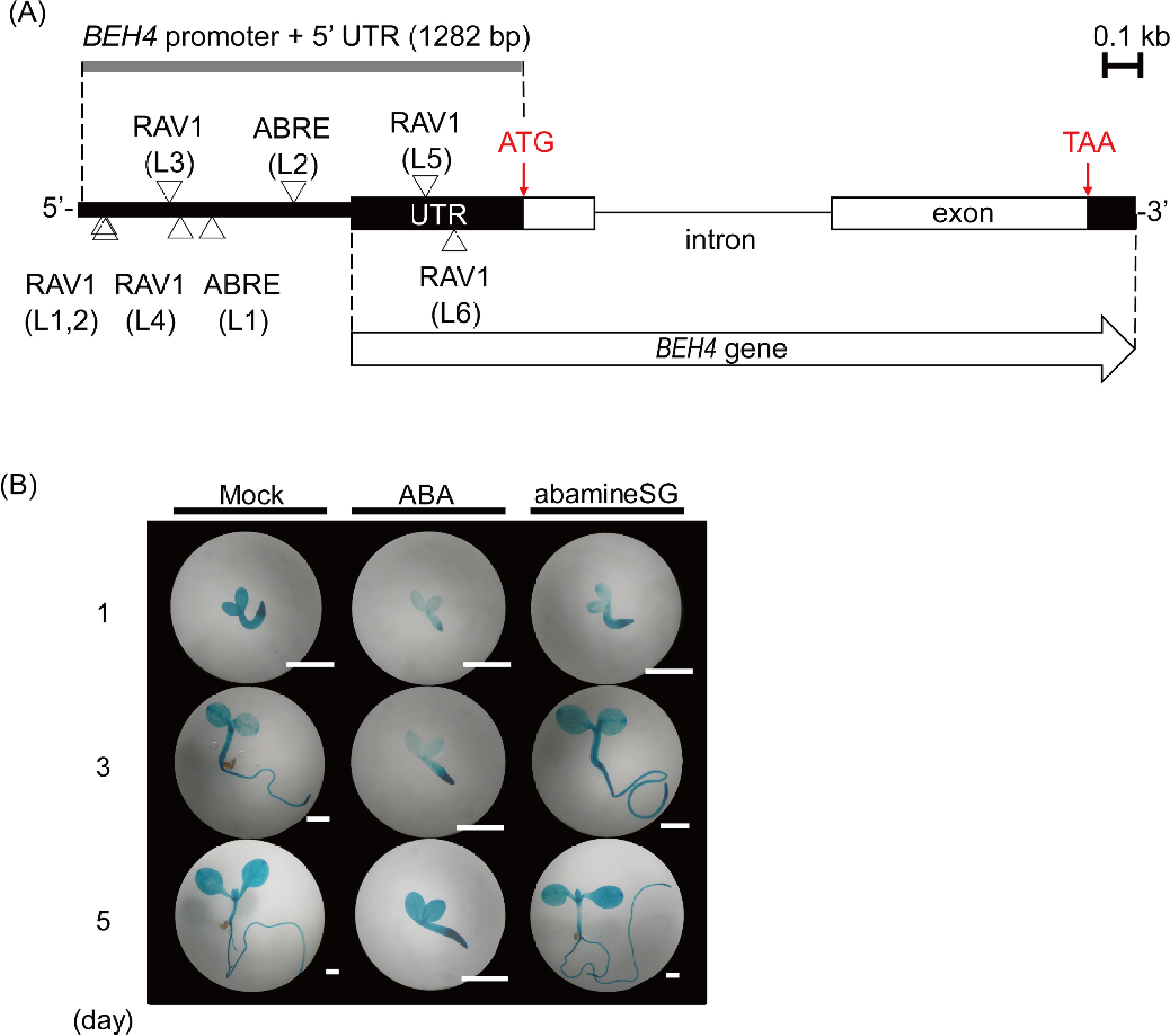
Fig. 6. The response of BEH4 to increased or decreased ABA levels was examined histochemically. (A) The triangles on a schematic drawing of the BEH4 gene and its 5′-flanking sequence show the positions of ABRE-like and RAV-like elements in both strands of the DNA double helix. The element sequences are presented in Table 2. Box, exon; thin line, intron; thick line, 5′-flanking (promoter) sequence; UTR, either 5′- or 3′-untranslated regions of BEH4. (B) BEH4::GUS transgenic seedlings were subjected to histochemical GUS staining; following the treatment of either ABA (1 µM) or abamineSG (50 µM), a specific inhibitor of ABA synthesis DMSO (0.1%) was applied to plants as a mock treatment. Scale bars represent 1 mm.