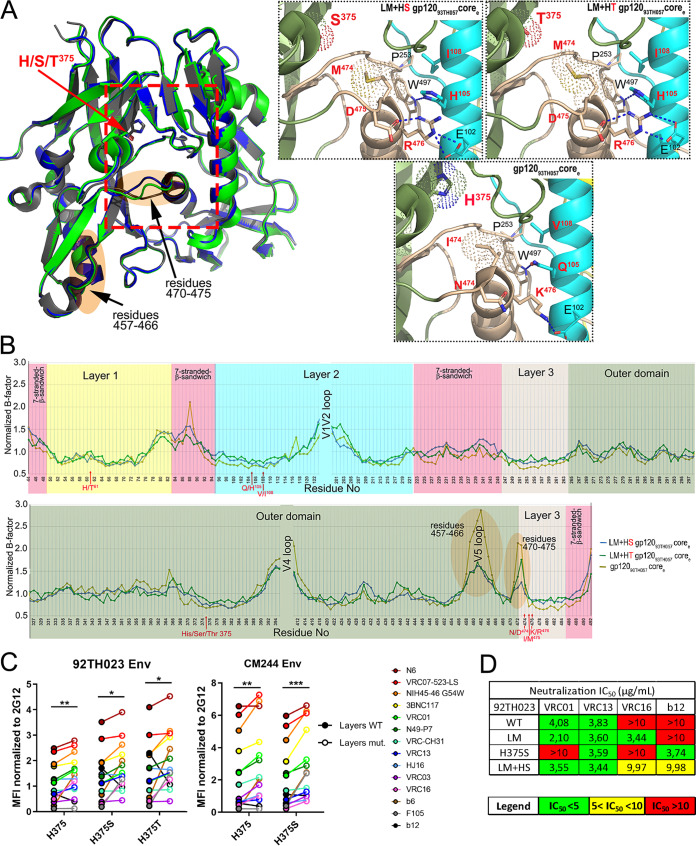
FIG 9.
Effect of gp120 layer mutations on the highly conserved CD4 binding site. (A) Structures of LM+HS and LM+HT gp12093TH057 unliganded corees are superimposed onto wild-type gp12093TH057 coree (PDB code: 3TGT). Residue 375 is shown as sticks, and the gp120 regions proximal to the CD4 binding site that shows the lowest B-factors in the LM core mutants compared to the unmutated core are highlighted in orange. The magnified views (right panel) show the network of interactions in each core mediated by LM+HS/T residues. The hydrogen bonds are shown as blue dashes. LM+HS/T residues are labeled in red. (B) Plot of the normalized B-factors for the main chain atoms of residues of coree structures. The rigidified region is highlighted in orange. (C) Cell surface staining of 293T cells transfected with CRF01_AE Env expressors (92TH023 and CM244 isolates [WT or their mutated counterparts]) using a panel of CD4-binding site antibodies (CD4BS Abs). Shown are the mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) normalized to 2G12 MFI obtained in the transfected (GFP+) population for staining obtained in at least 3 independent experiments. All MFI data were normalized to 2G12 MFI for each Env mutant. Error bars indicate means ± SEM. Statistical significance was tested using a paired t test or a Wilcoxon signed-rank test based on statistical normality (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (D) Recombinant HIV-1 strains expressing luciferase and bearing wild-type or mutant CRF01_AE Envs (92TH023 and CM244 isolates) were normalized by reverse transcriptase activity. Normalized amounts of viruses were incubated with serial dilutions of VRC01, VRC16, VRC13, or b12 at 37°C for 1 h prior to infection of Cf2Th-CD4/CCR5 cells. Neutralization half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) data are summarized.