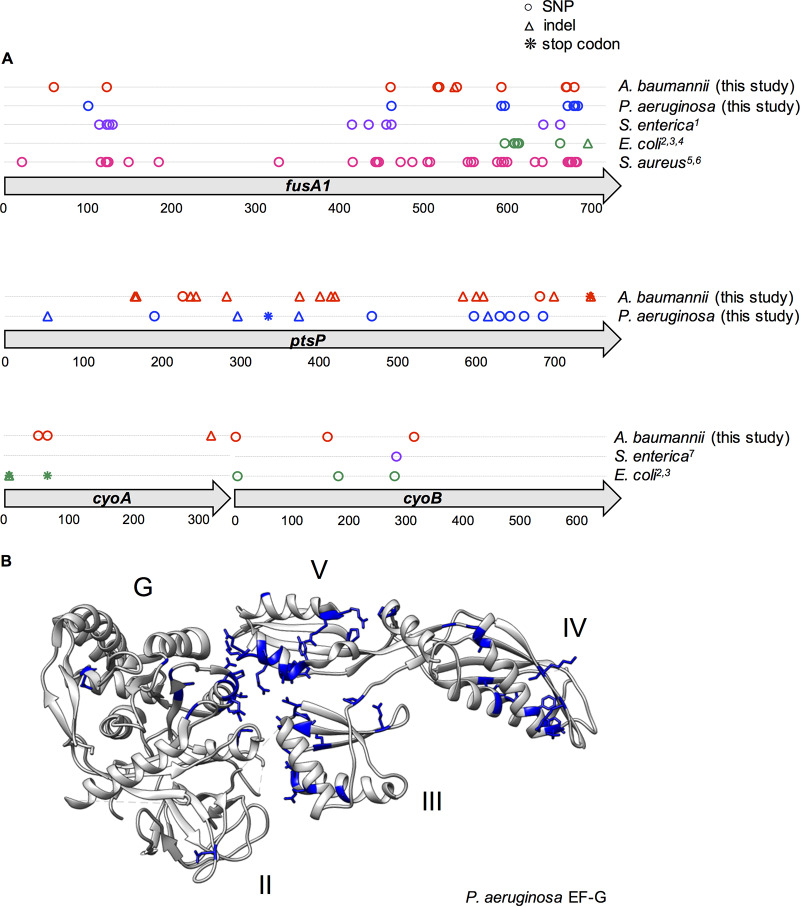
FIG 4.
Parallelism of mutations in genetic loci associated with aminoglycoside resistance across species. (A) All mutations that occurred at any point in the experiment within the fusA1, ptsP, cyoA, or cyoB gene are indicated by a symbol at their position within the consensus amino acid sequence. Mutations reported in previous literature in other species are indicated and color coded by species; these mutations were either selected by aminoglycoside treatment in vitro or selected by another antibiotic and subsequently demonstrated to confer resistance to aminoglycosides. SNPs are indicated by circles, insertions or deletions (indels) are indicated by triangles, and stop codon mutations are indicated by asterisks. For each gene, the encoded amino acid sequences for all species in which mutations were identified were aligned. Mutations are shown according to their position in the resulting consensus amino acid sequence. (Top) fusA1 gene; (middle) ptsP gene; (bottom) cyoA and cyoB genes. The referenced literature is identified as follows: 1, Johanson and Hughes (38); 2, Jahn et al. (49); 3, Ibacache-Quiroga et al. (7); 4, Mogre et al. (51); 5, Kim et al. (50); 6, Norström et al. (52); 7, Wistrand-Yuen et al. (26). (B) Amino acid positions that were mutated in any species are shown in blue on the protein structure of the strain PAO1 EF-G (56). Mutations are shown according to their corresponding position in the P. aeruginosa EF-G amino acid sequence. Domains G (GTPase), II, III, IV, and V are indicated.