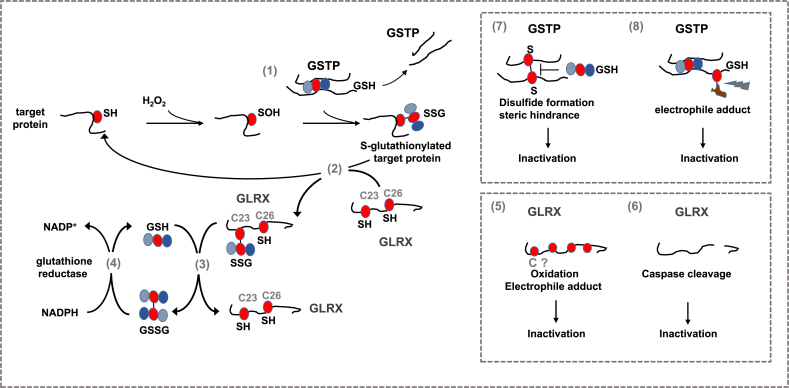
Fig. 1.
Steps in the catalytic cycle of protein S-glutathionylation (PSSG) and deglutathionylation believed to be relevant in the pathogenesis of chronic lung diseases. A number of biochemical events can induce PSSG. The mode of PSSG is likely to be target and context specific, dependent upon the proximity of oxidant producing enzymes, redox relays, the oxidation state of the GSH/GSSG redox couple etc. In epithelial cells in settings of a pro-fibrotic environment, oxidants originating from multiple sources lead to a sulfenic acid intermediate (SOH) which can be a platform for subsequent PSSG, which can happen spontaneously or catalyzed by glutathione S- transferases (GST), notably GSTP [1]. Conversely GLRX acts to deglutathionylate proteins [2], restoring the original sulfhydryl group. GLRX induces deglutathionylation via the monothiol mechanism requiring only the N-terminal cysteine in the thioredoxin (TXN) domain [2], which can thereafter be reduced by reduced glutathione (GSH) [3] re-establishing the reduced thiol group of the N-terminal cysteine in GLRX. Glutathione disulfide (GSSG), formed in this process can be reduced back to GSH through the action of glutathione reductase (GR) consuming reducing equivalents form NADPH [4]. GLRX can be inactivated via oxidations of one or more cysteines outside of the TXN domain [5] including electrophiles from cigarette smoke. GLRX can also directly cleaved by caspases 8 and 3 [6]. Similarly, GSTP also is subject to oxidant-mediated inactivation, potentially involving a disulfide which creates steric hindrance that interferes with GSH binding [7], or electrophile-induced modification [8]. We refer the reader to the body of text for detailed information. Red circle: protein cysteine or cysteine in glutathione. SH: reduced cysteine, SOH: Sulfenic acid, SSG: S-glutathionylated protein, GSH: Reduced glutathione, GSSG: glutathione disulfide, comprised of two glutathione molecules with a disulfide bond between the cysteines of each glutathione molecule, S–S: disulfide. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)