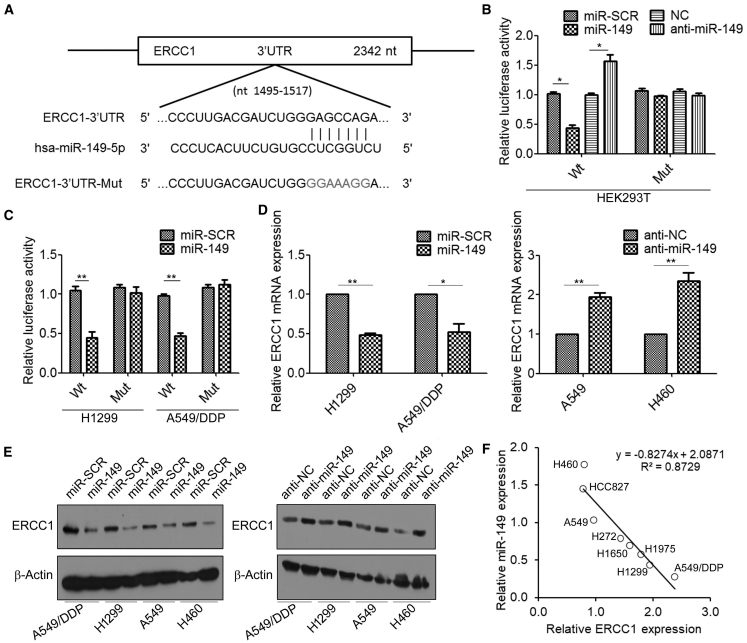
Figure 6.
ERCC1 Is the Direct Target of miR-149
(A) TargetScan 7.2 predicted miR-149-binding sites in the 3′ UTR of ERCC1. Wild-type (WT) and mt 3′ UTR of ERCC1 were cloned into a luciferase reporter plasmid, respectively. (B) HEK293T cells were co-transfected with WT or mt ERCC1-3′ UTR-luciferase reporter constructs and miR-scramble control (miR-SCR) or miR-149 mimics and anti-miR negative control (anti-NC) or anti-miR-149, respectively; the relative luciferase activities were measured 48 h after transfection. Firefly luciferase activity of the reporters was normalized to the internal Renilla luciferase activity. (C) H1299 and A549/DDP cells were co-transfected with WT or mt ERCC1-3′ UTR-luciferase reporter constructs and miR-SCR or miR-149 mimics for 48 h; the relative luciferase activities were measured 48 h after transfection. (D) H1299 and A549/DDP cells were transfected with miR-SCR or miR-149 mimics, A549 and H460 cells were transfected with anti-NC or anti-miR-149, and the mRNA levels of ERCC1 were measured by real-time RT-PCR. (E) H1299, A549/DDP, A549, and H460 cells were transfected with miR-SCR or miR-149 mimics (left) and anti-NC or anti-miR-149 (right), and the expression levels of ERCC1 were measured by western blotting. (F) Correlation of ERCC1 and miR-149 expression levels in eight NSCLC cell lines. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.