Fig. 5 |. Genetic validation of ZIP7 as the target of NVS-ZP7–4.
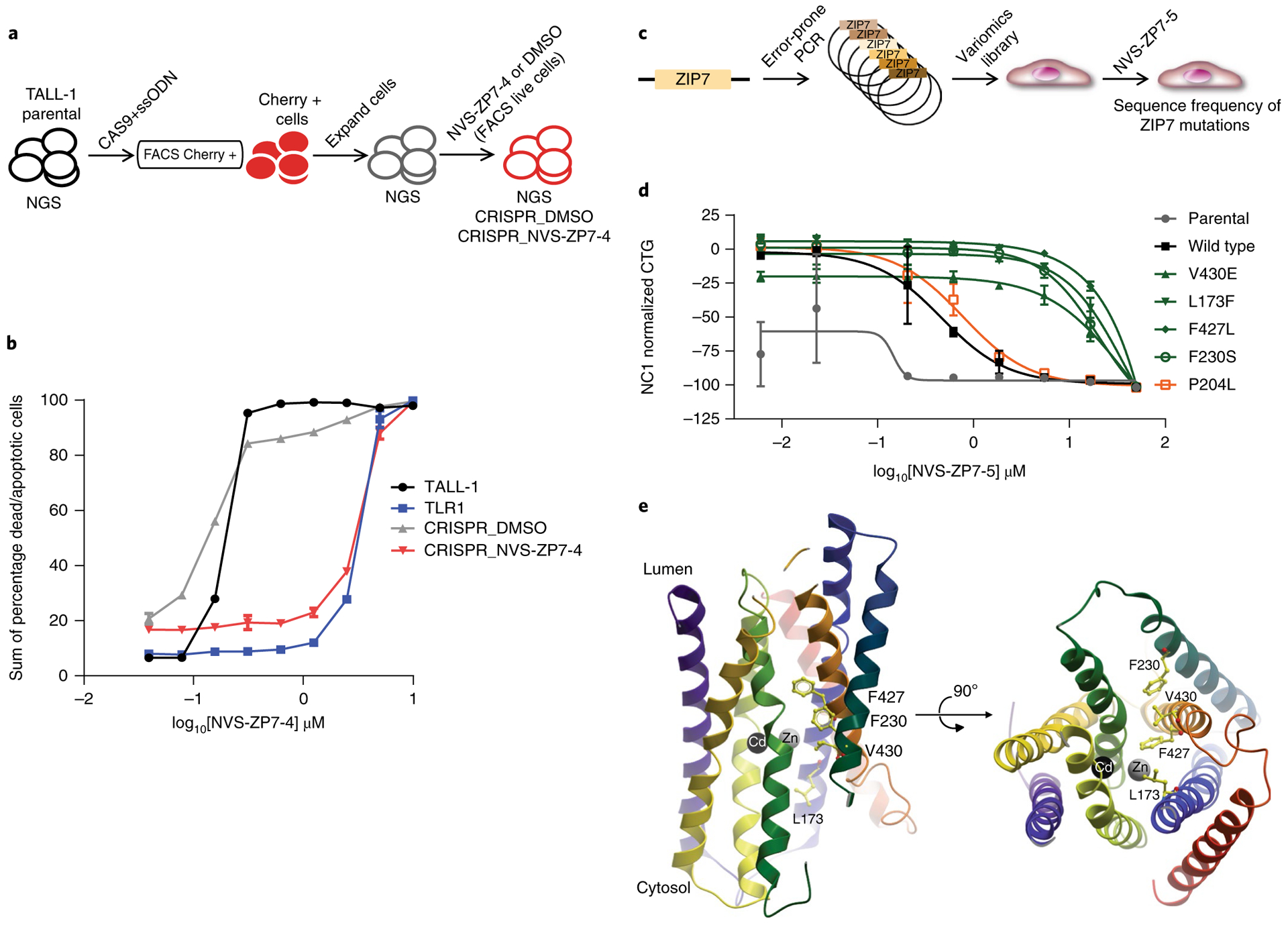
a, Schematic of the process to generate the ZIP7 V430E CRISPR knock-in cell line in the TALL-1 cellular background. b, Effect of 72 h of NVS-ZP7–4 treatment on apoptosis/cell death as measured by annexin V/propidium iodide staining in TALL-1 cells, spontaneous resistant TLR1 cells, as well as TALL-1 cells, following introduction of the ZIP7 V430E mutation with CRISPR and short-term selection with either DMSO (CRISPR_DMSO) or NVS-ZP7–4 (CRISPR_NVS-ZP7–4). Data shown are the sum of percentage dead and apoptotic cells by annexin V/propidium iodide staining after compound treatment. The x–y line graph represents the data from one individual experiment in which two independent samples are treated with compound. The average readout value for these samples is represented by the points and connecting lines with standard error bars. This exact experiment was performed two independent times. c, Schematic of process to generate ZIP7 variomics library and identify mutations that confer resistance to NVS-ZP7 compounds. d, Effect of 72 h of NVS-ZP7–4 treatment on proliferation (CTG) of parental HSC-3 cells or HSC-3 cells expressing wild type or mutant ZIP7 (V430E, L173F, F427L, F230S, P204L). Error bars represent s.d. of the mean from three biological replicates (n = 3) in an individual experiment. Each experiment was performed two independent times. e, Homology model of hZIP7 on the basis of the crystal structure of bacterial zinc transporter ortholog BdZIP (PDB code 5TSA) with transmembrane helices shown as ribbons. Zinc and cadmium ions at the binuclear center of the transporter are shown as gray and black spheres, respectively. Mutations that confer resistance to NVS-ZP7 compounds are shown in yellow ball-and-stick representation. Rotated view (right panel) is also shown.
