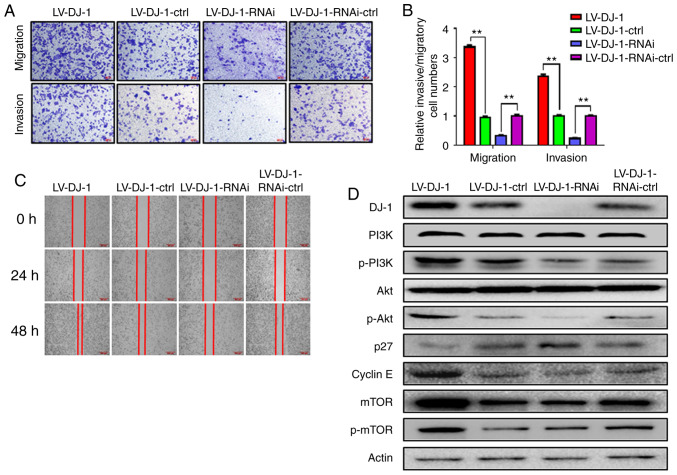
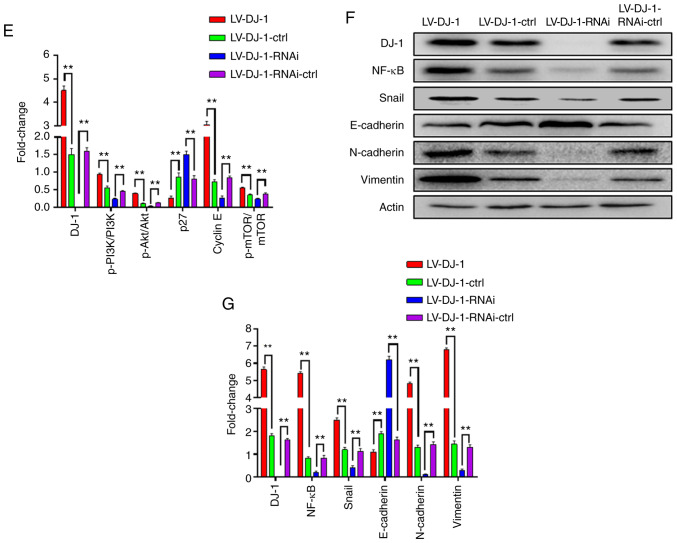
Figure 4.
DJ-1 positively regulates CRC cell migration and invasion in vitro. (A and B) The cell migration and invasion results of HCT116 cells with differential DJ-1 expression levels. Numbers of cell migration and invasion per field were counted in five random fields for the DJ-1-overexpressing/knockout and control groups (n=3/group). The ability of cell migration and invasion was increased after DJ-1 over-expression, whereas the ability of cell migration and invasion was decreased after DJ-1 knockout (**P<0.01). (C) Wound healing assay was used to detect the migratory ability of HCT116 cells with differential DJ-1 expression levels. The wound healing rate of LV-DJ-1 cells was higher than that of the LV-DJ-1-ctrl cells, whereas the wound healing rate was lower in the LV-DJ-1-RNAi cells compared with the control groups. (D and E) The expression of PI3K/Akt downstream molecules such as p27, cyclin E, mTOR, p-mTOR was detected by western blot analysis. DJ-1 regulated PI3K/Akt/p27/cyclin E and PI3K/Akt/ mTOR signaling pathway to promote CRC cell growth and metastasis. Densitometric analysis is presented as mean ± SD of 3 separate experiments (**P<0.01). (F and G) Nuclear transcription factors (NF-κB, Snail), EMT markers (E-cadherin, N-cadherin, and vimentin) were evaluated by western blot analysis. Densitometric analysis is presented as mean ± SD of 3 separate experiments (**P<0.01). DJ-1 was able to regulate the NF-κB/Snail signaling pathway to induce EMT. CRC, colorectal cancer; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition. The HCT116 cells were infected with lentivirus (LV)-DJ-1, LV-DJ-1-control (ctrl), LV-DJ-1-RNA interference (RNAi) and LV-DJ-1-RNAi-ctrl.