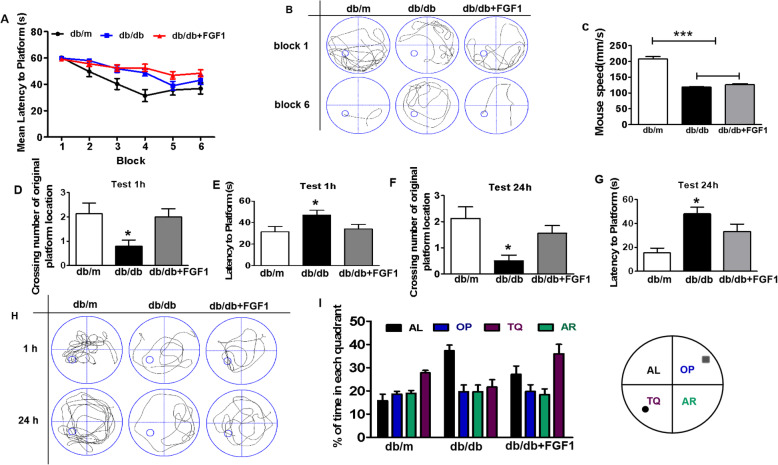
Fig. 2.
Exogenous FGF1 ameliorates DICD with inferior learning and memory function. a The learning curve of training period of mice during 6 blocks in the Morris water maze test; b Representative swimming track of mice at block 1 and block 6 during training period; c Swimming speed of mice in db/m, db/db and db/db + FGF1-treated mice during Morris water maze test; d Number of crossing over the original platform location of mice in probe trial (1 h after training); e Latency time to find the platform of mice in probe trial (1 h after training); f Number of crossing over the original platform location of mice in probe trial (24 h after training); g Latency time to find the platform of mice in probe trial (24 h after training); h Representative swimming track of mice in probe trial (1 h and 24 h after training); i Percentage of residence time in each quadrant of mice. The quadrant with platform was designated as TQ and the quadrant from which the mice started their swimming was designated as OP for “opposite”; The quadrant on the left side of OP was designated as AL for “adjacent left” and the quadrant on the right side of OP was designated as AR for “adjacent right”. *p < 0.05 vs. db/m mice and db/db + FGF1-treated mice, ***p < 0.001 vs. db/db mice and db/db + FGF1-treated mice, n = 10