Fig. 3.
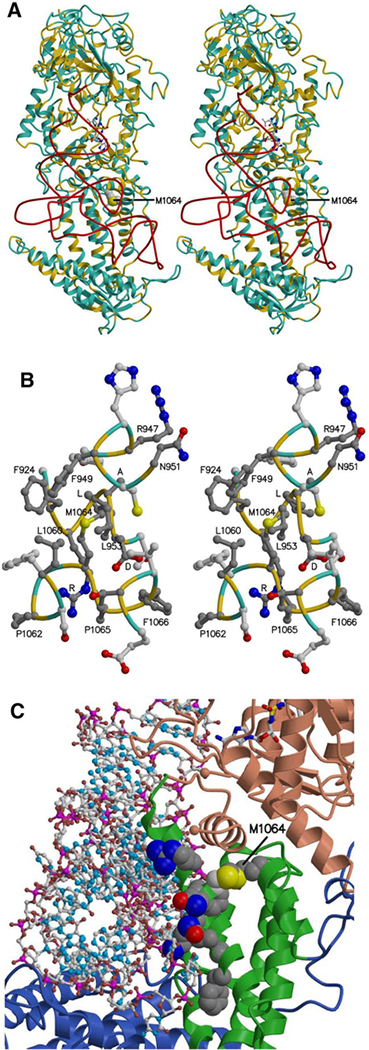
The model of human valyl-tRNA synthetase with tRNA ▸ bound. a, b The protein main chain (alpha-carbon atoms) is colored according to sequence identity with the template structure, yellow where identical (39%) and light blue where different. a Stereo view, with the tRNA backbone (phosphorus atoms) shown in red, a Val-AMP analog shown as ball and stick, bound in the aminoacylation site, and the side chain of Met 1064 shown as space filling. The location of an unmodeled region inserted in the human sequence between the KMSKS loop and the DALR motif is marked by the blue spheres representing Asp 875 and Cys 917. b Stereo view of residues neighboring Met 1064, with carbon atoms in side chains of residues identical in the model and template colored dark gray. The DALR motif and other conserved residues are labeled. For clarity, only the tip of Leu 953 is shown. c Protein-tRNA interface, with tRNA shown as ball and stick and the Val-AMP analogue shown as sticks. The possible impact of the M1064I mutation on ValRS-tRNA binding is illustrated by showing side chains as space filling for Met 1064 and Cys 950, as well as for conserved residues at or near the interface: Arg 947, Phe 949, Asn 951, Lys 952, Asn 955, Ala 956, and Phe 959. The M1064I mutation might also perturb the interface between the catalytic core domain (colored salmon) and the anticodon-binding domain (green)