Figure 1.
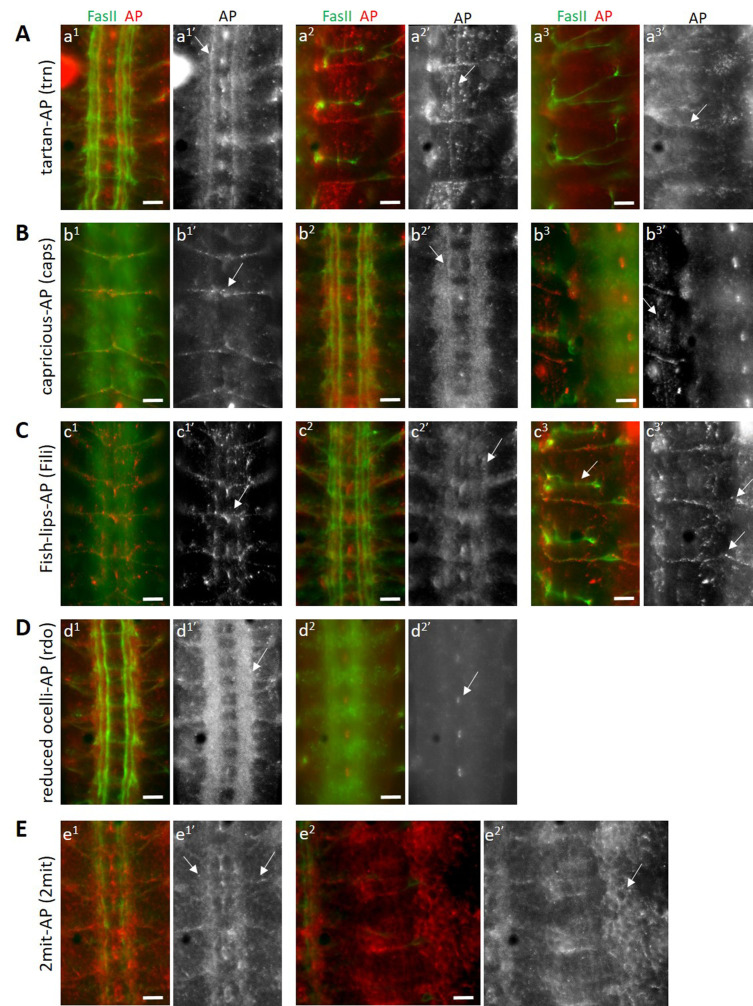
Binding patterns of eLRR AP fusion proteins. All embryos are double-stained for FasII (green) and AP (red). (A) Binding pattern of trn-AP. a1’ shows trn-AP binding to longitudinal axons in the VNC, with stronger binding to one particular axon bundle (arrow). a2’ shows trn-AP binding to muscle targets (arrow). a3’ shows sensory axons labeled by trn-AP. (B) Binding pattern of caps-AP. b1’ shows a set of midline neurons labeled by caps-AP. b2’ shows caps-AP binding to longitudinal axons with one axon bundle showing stronger binding (arrow). b3’ shows caps-AP binding to muscles (arrow). (C) Binding pattern of Fili-AP. c1’ shows Fili-AP binding to dorsal midline neurons (arrow). c2’ shows Fili-AP binding to a subset of longitudinal axons. c3’ shows Fili-AP binding to the transverse nerve (arrow). (D) Binding pattern of rdo-AP. d1’ shows strong rdo-AP binding to longitudinal, commissural and exiting motor axons in the VNC. d2’ shows rdo-AP binding to midline glial cells. (E) Binding pattern of 2mit-AP. e1’ shows 2mit-AP binding to longitudinal axons and exiting motor axons in the VNC (arrows). Strong binding is also seen to midline cells and fainter staining is seen on the surface of other cells in the VNC. e2’ shows 2mit-AP binding to the surface of cells in the periphery (arrow). Scale bars, 10µm.