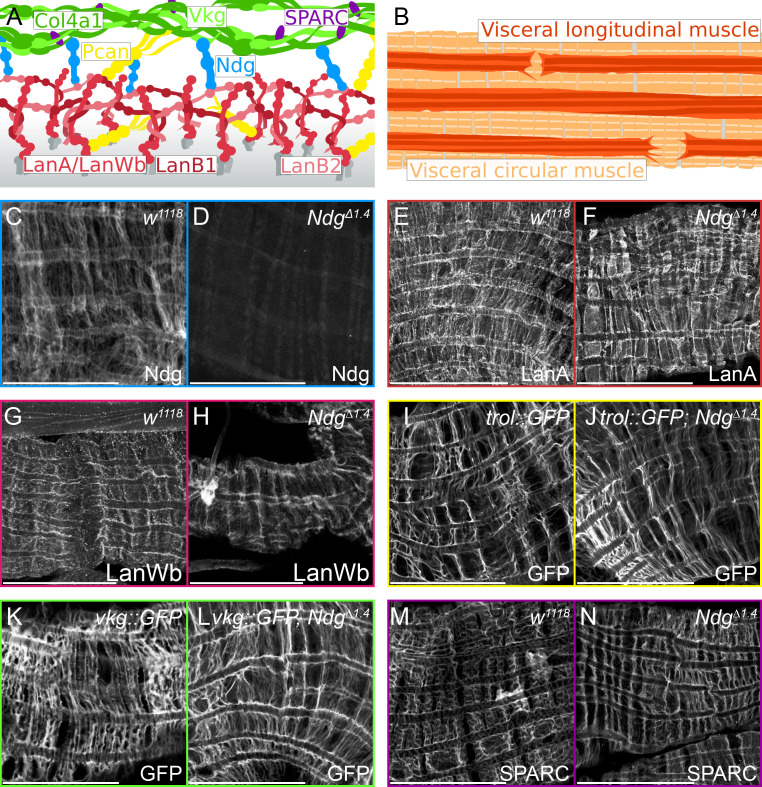
Figure 1.
Distribution of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins in the visceral midgut muscles of Ndg mutant larvae. (A) Schematic illustration of ECM core components. Laminin heterotrimers are anchored to cell surface receptors and are organized as a network building ternary nodes. The Laminin A and Laminin Wb heterotrimers are composed of either the α-subunit Laminin A (LanA, red) or the α-subunit Laminin Wb (LanWb, red), the β-subunit Laminin B1 (LanB1, dark red) and the γ-subunit Laminin B2 (LanB2, light red). Collateral linkage between the ECM networks is mediated by Perlecan (Pcan, yellow; encoded by the trol gene) as well as Nidogen (Ndg, blue), that binds to Laminin, Perlecan and Collagen IV. The Collagen IV triple helix is composed of two α1- subunits (Collagen IV α1, Col4α1, dark green) and one α2-subunit (Viking, Vkg, light green). Secreted protein, acidic, cysteine-rich (SPARC, purple) binds to the Collagen IV network. (B) Schematic illustration of the larval midgut visceral muscle morphology. Circular muscles highlighted in light orange and overlaying longitudinal muscles in dark orange. (C, D) Nidogen antibody staining in control (white1118, C) and NdgΔ1.4 mutant larvae (D). (E, F) Laminin A and (G, H) Laminin Wing blister antibody staining in control (white1118, E and G) and NdgΔ1.4 mutant larvae (F and H). (I, J) GFP antibody staining in control (trol::GFP, I) and Ndg mutant (trol::GFP; NdgΔ1.4, J), (K, L) as well as in control (vkg::GFP, K) and Ndg mutant larvae (vkg::GFP, NdgΔ1.4, L). (M, N) SPARC antibody staining in control (white1118, M) and NdgΔ1.4 mutant larvae (N). Scale bars = 50 µm.