Figure 5.
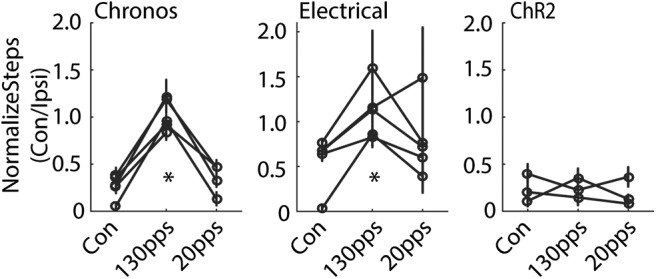
Behavioral effects of STN DBS on forelimb adjusting steps in hemi-parkinsonian rats. Left, High-rate optogenetic STN DBS at 130 pps in Chronos-injected rats increased the ratio of contralateral-to-ipsilateral limb use, indicating an increase of impaired forelimb use. Low-rate optogenetic STN DBS at 20 pps in Chronos-injected rats had no effect (p < 0.001, one-way repeated measures ANOVA, n = 5). Middle, High-rate STN electrical DBS increased the ratio of contralateral-to-ipsilateral limb use, but low rate electrical DBS did not (p < 0.001, n = 5). Right, Optical STN DBS in ChR2-injected rats did not generate behavioral effects (p = 0.527, n = 3); *p < 0.001. Data are mean ± SE.
