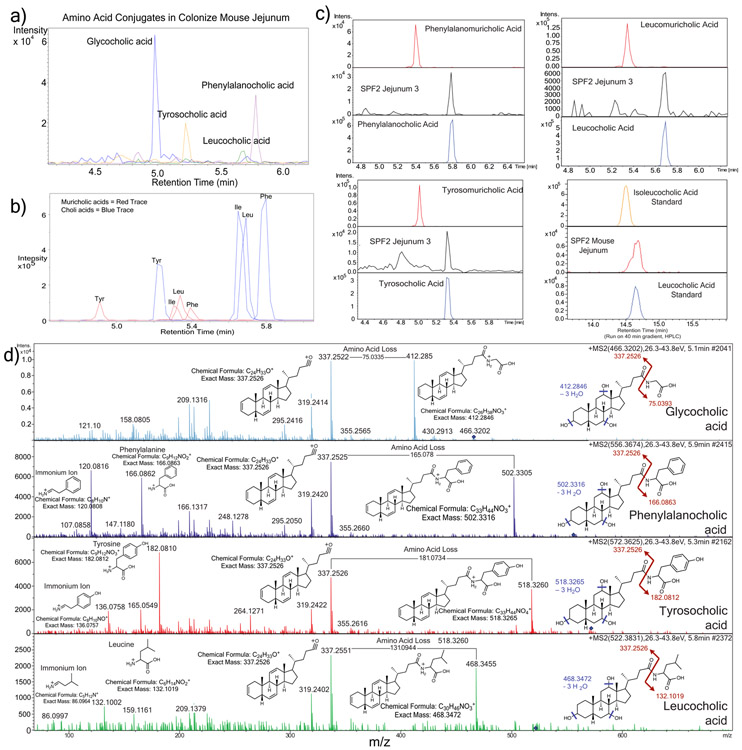
Extended Data Fig. 5. Mass spectrometry analysis of novel conjugated bile acids.
a) Extracted ion chromatogram MS1 traces of Tyr-chol (m/z 572.37 +/− 0.05 Da), Phe-chol (m/z 556.37 +/− 0.05 Da) and Leu-chol (m/z 522.37 +/− 0.05 Da, experiments performed four times). b) Extracted ion chromatograms for the synthetic muricholic and cholic acid versions of the Phe- (m/z556.37 +/−0.05), Tyr- (572.37 +/−0.05) and Leu- (522.37 +/−0.05) conjugates showing the different retention times from the muricholic and cholic acid forms. c) Retention time alignments of novel synthetic muricholic and cholic acid conjugates with the novel conjugates found those found in a colonized murine jejunum sample. The isoleucocholic and leucocholic acid analysis was run on a long gradient HPLC column to separate isomeric ile/leu conjugates and compare to that detected in vivo. d) Annotation of MS/MS fragmentation patterns for the 3 novel conjugated bile acids discovered in this manuscript and GCA. Structures of the immonium ions from amino acid fragmentation, whole amino acid fragments and major sterol fragment are shown. Loss of the amino acid mass on the bile acid steroid backbone is also highlighted.