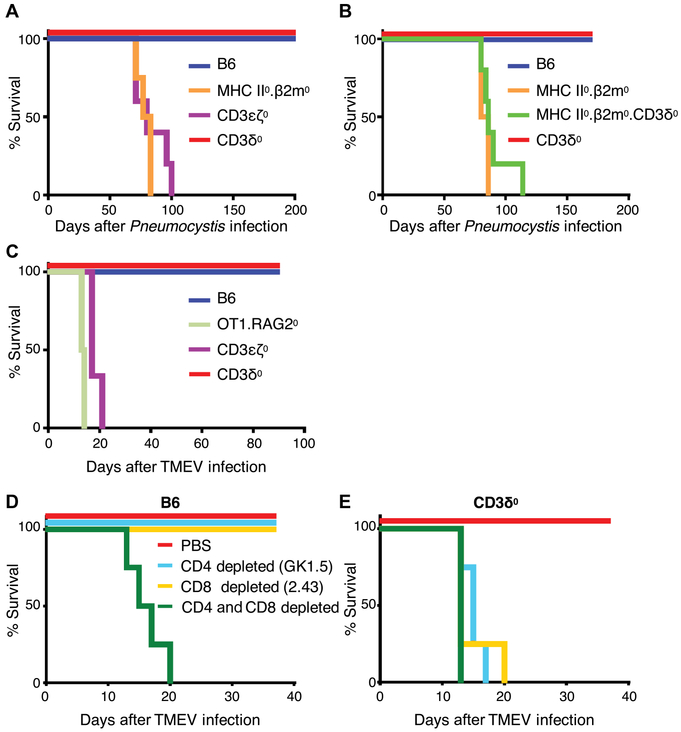
Fig. 8. T cells in CD3δ0 mice provide immune activity against PCP and TMEV.
(A) To assess the extent of T cell immune activity in a CD3δ0 setting, we infected mice from the listed genotypes with P. murina (mouse n ≥ 4 per genotype). Kaplan-Meier curves display survival defined by mice being euthanized upon loss of 20% weight, where CD3δ0 was statistically different from susceptible genotypes (P ≤ 0.004) by log-rank Mantel-Cox tests. (B) To test the role of MHC in mediating protection from PCP in CD3δ0 setting, mice from the listed genotypes were infected with PCP (mouse n ≥ 4 per genotype). Kaplan-Meier curves display survival defined by mice being euthanized upon loss of 20% weight, where CD3δ0 and MHC II0.β2m0.CD3δ0 were statistically different (P = 0.0018) by log-rank Mantel-Cox test. (C) Mice from the listed genotypes were infected with TMEV [mouse n ≥ 4 for all genotypes, except for CD3ε0ζ0 (n = 3)]. Kaplan-Meier curves display survival defined by mice being euthanized upon immobilization due to functional deficit or loss of 20% weight, where CD3δ0 was statistically different from susceptible genotypes (P ≤ 0.01) by log-rank Mantel-Cox tests. (D and E) To assess CD4 and CD8 T cell immune activity, B6 and CD3δ0 mice were either depleted of CD4 cells with GK1.5 anti-CD4 mAb injections, depleted of CD8 cells with 2.43 anti-CD8 mAb injections, depleted of both CD4 and CD8 cells, or PBS-control injected as indicated, and were infected with TMEV [mouse n = 4 for all groups, except for CD3δ0 + PBS (n = 3)]. Kaplan-Meier curves display survival defined by mice being euthanized upon immobilization due to functional deficit or loss of 20% weight, where CD3δ0 + PBS was statistically different from any of the three subset-depleted conditions (P < 0.02) by log-rank Mantel-Cox tests.