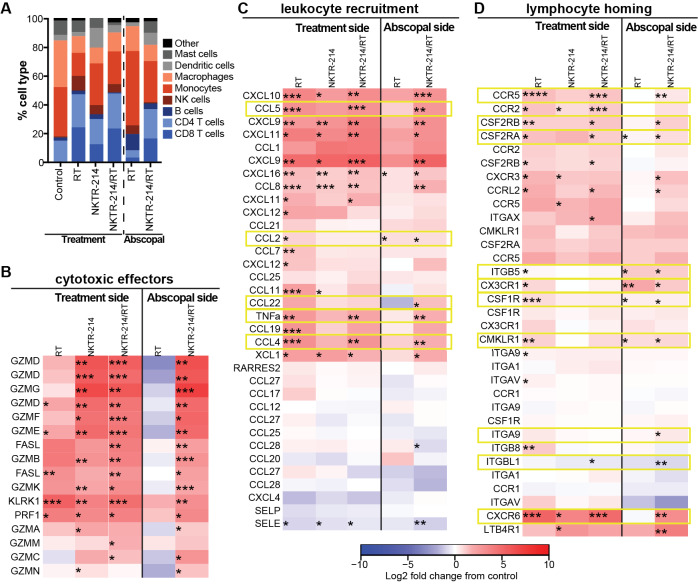
Figure 5.
RT increases lymphocyte homing genes on the treatment and abscopal sides. Eight days post-treatment, tumors from CT26-bearing mice were processed for RNA isolation for gene expression analysis with Mouse Affymetrix 430 2.0 arrays (n=3 biological replicates per group). Not false discovery rate corrected prior to statistical analysis. (A) CIBERSORT analysis of the RNA indicates an expanded proportion of CD8+ T cells in the treatment and abscopal tumors from mice that received NKTR-214/RT combination treatment. (B, C, D) Change in gene expression compared with vehicle control are shown for RT, NKTR-214, or the NKTR-214/RT combination group. vehicle control is the reference for all log fold-changes and thus is not shown separately. RT enhances expression of leukocyte recruitment and lymphocyte homing genes both alone and in combination with NKTR-214. RT and NKTR-214 alone can induce genes related to lymphocyte homing on the treatment side, but only RT can induce those genes on the abscopal side. NKTR-214 alone induces systemic cytotoxic effector genes. Thus, combination of NKTR-214/RT increases homing and recruitment of active CD8+ T cells that reduce tumor burden. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001. RT, radiotherapy.