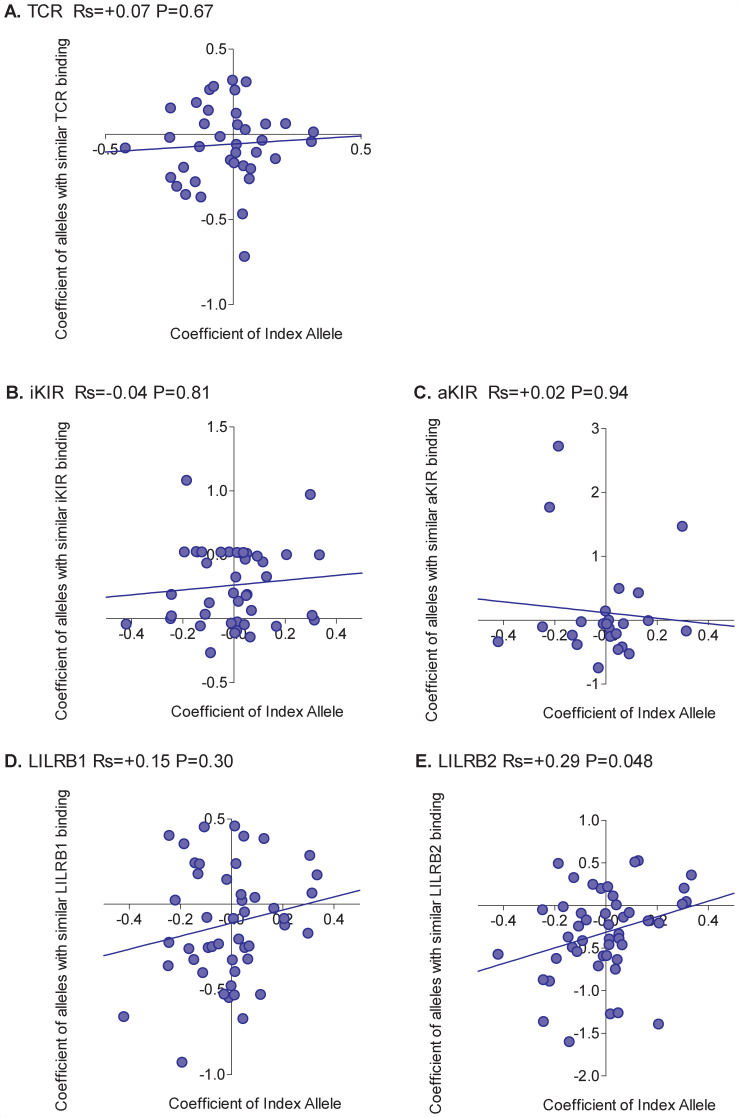
Appendix 4—figure 3. Correlation between the HIV-1 viral load associated with an allele and the viral load associated with similar alleles.
The early viral load set point associated with an HLA class I allele ('Coefficient of Index Allele, x axis) was correlated with the coefficient of HLA class I alleles with similar TCR binding (A), similar iKIR binding (B), similar activating KIR binding (C), similar LILRB1 binding (D) and similar LILRB2 binding (E). All alleles in the cohort of a sufficient frequency (N > 15) and with sufficient near alleles (N > 15 with 50% or more similarity) were considered. The Spearman correlation coefficient (Rs) and corresponding P value are reported in the title bar for each plot. Unlike HTLV-1 infection, and more in line with expectation, the picture was mixed with no single interaction able to explain all HLA associations. The only significant correlation was between the protection offered by an alleles and the protection offered by alleles with similar LILRB2 binding (E). However, the correlation was weak and there were plenty of alleles which did not conform to the pattern.