Figure 1. Key glutamate residues in CLC transporters.
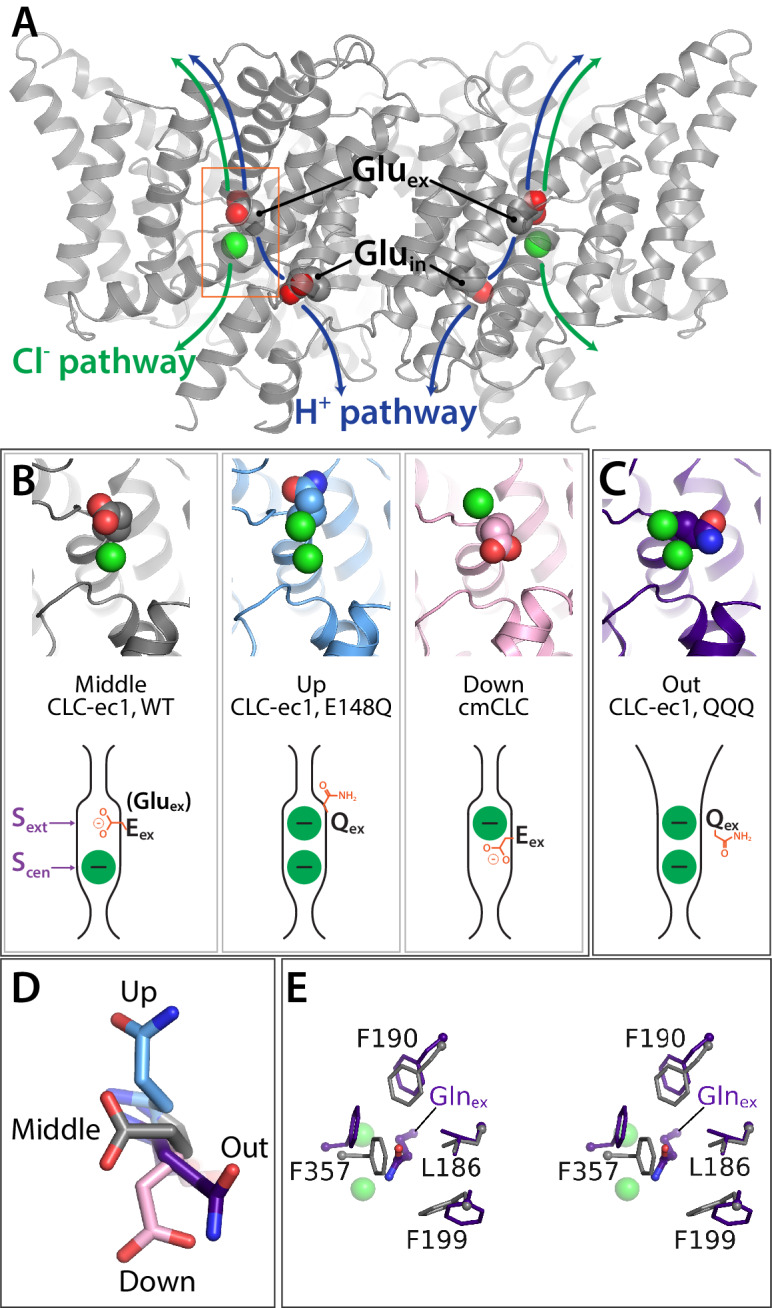
(A) CLC-ec1 wild-type structure (PDB 1ots) showing the external and internal glutamate residues (Gluex and Gluin) in the two subunits of the homodimer. Chloride ions are shown as green spheres. Each subunit independently catalyzes Cl–/H+ exchange. The approximate transport pathways for these ions are indicated with green and blue arrows. The orange box frames the close-up view (shown in panel B) of the Cl–-binding sites along with Gluex. (B) Gluex conformations observed in CLC transporters. Three panels showing structures (top panels) and cartoon representations (bottom panels) depicting the three conformations (‘middle’, ‘up’, and ‘down’) adopted by Gluex in various CLC structures, WT (1ots), E148Q (1otu), and cmCLC (3org). The Sext and Scen anion-binding sites are labeled in the WT cartoon at left. (C) QQQ structure reveals a new conformation for Gluex. Structure and cartoon representations as in panel B. (D) Overlay of Gluex/Glnex conformations seen in QQQ (purple), E148Q (blue), WT (grey) and cmCLC (pink). (E) Overlays (stereoview) of WT (grey) and QQQ (purple) illustrate changes in positioning of conserved residues near Gluex.
