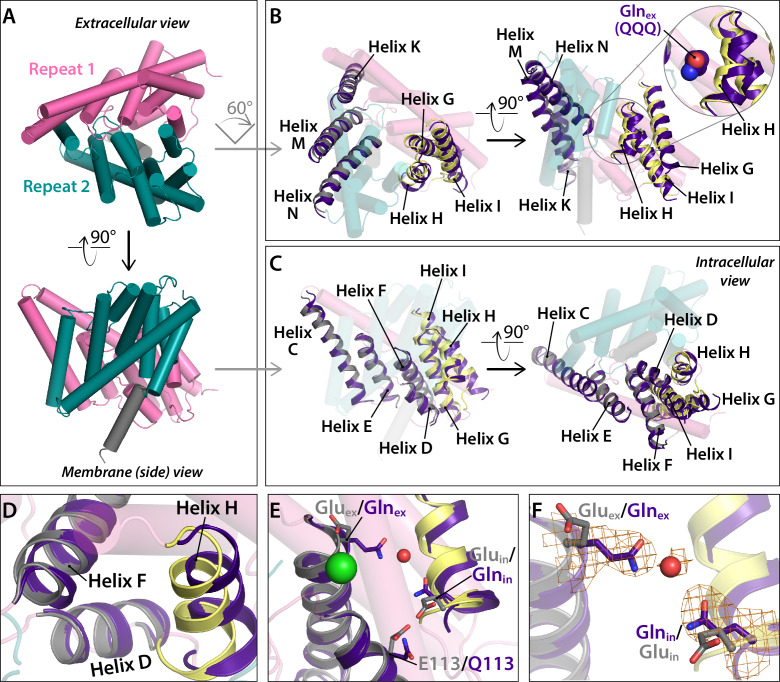
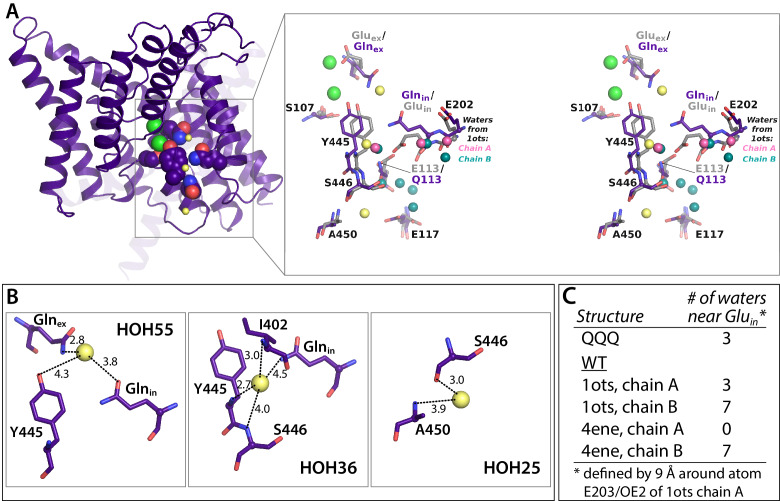
Figure 6. Conformational change at Helices G-I and repositioning of Glnin (Helix H).
(A) View of one CLC subunit, highlighting Repeat 1 in pink and Repeat 2 in teal. Helix R (not part of the repeats) is shown in grey. (B) Movement of Helices G-I (part of Repeat 1) relative to Helices K, M, N (Repeat 2). The compared helices are shown in ribbon, with QQQ in purple and WT in gray (Helices K, M, N) or yellow (G–I). Other helices (WT) are shown as transparent cylinders. The inset illustrates how the movement of Helix H away from Helix N creates space to avoid steric conflict with Glnex in the ‘out’ position. (C) Movement of Helices G-I relative to other helices in Repeat 1. The compared helices are shown in ribbon, with QQQ in purple and WT in gray (Helices C-E) or yellow (G–I). Other helices (WT) are shown as transparent cylinders. (D) Close-up view showing movement of Helix H (containing Glnin) away from Helix D. (E) Conformational change at Glnin moves it away from Q113. (F) Movement of Glnin to the hydrophobic core of the protein brings it to within 6 Å of Glnex. Electron density for Glnex, Glnin, and an intervening water molecule is shown in mesh.