Figure 4.
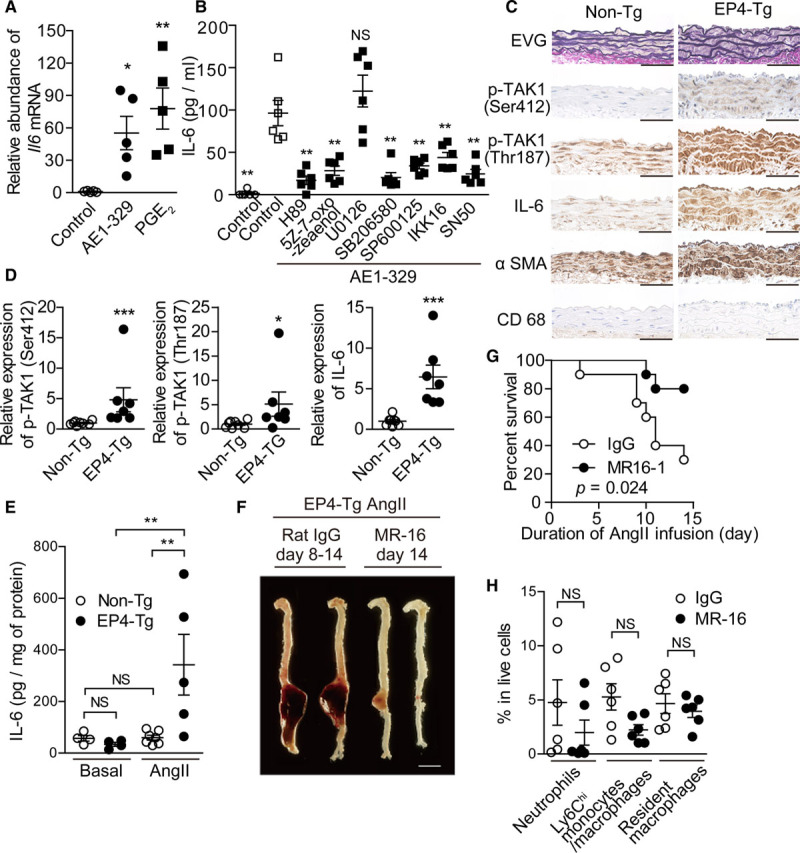
EP4 (prostaglandin E receptor 4)-PKA (protein kinase A)-TAK1 (transforming growth factor-β–activated kinase 1) and NF-κB (nuclear factor-kappa B) pathway increased IL (interleukin)-6 production and IL-6 inhibiton attenuated Ang II (angiotensin II)–induced abdominal aortic aneurysm. A, Expression of Il6 mRNA in EP4-Tg aortic vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) stimulated with EP4 agonist and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). n=5. B, IL-6 protein expression was measured by ELISA in EP4-Tg aortic VSMCs stimulated with the indicated drugs. n=6. C, Elastica van Gieson–stained (EVG) and immunohistochemically stained sections of the abdominal aortas of nontransgenic (non-Tg) and EP4-Tg mice after Ang II infusion. Scale bars=50 μm. D, Semiquantitative analysis of C. n=7 to 8. E, IL-6 protein expression was measured by ELISA in abdominal aorta from EP4-Tg before and after Ang II infusion. n=4 to 7. F, Representative images of aorta from Ang II–infused EP4-Tg treated with MR16-1. Scale bars=5 mm. G, Survival rates of Ang II–infused EP4-Tg treated with MR16-1 or control rat IgG. H, The number and proportion of cells in each gate from fluorescence-activated cell sorting analysis of abdominal aorta from Ang II–infused EP4-Tg at day 4. n=6. NS indicates not significant; and αSMA, alpha smooth muscle actin. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
