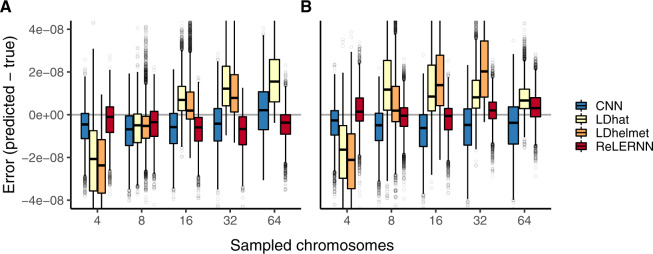
Fig. 4.
(A) Distribution of raw error () for each method across 5,000 simulated chromosomes after model misspecification. For the CNN and ReLERNN, predictions were made by training on equilibrium simulations while testing on sequences simulated under a model of population size expansion or (B) training on demographic simulations while testing on sequences simulated under equilibrium. For LDhat and LDhelmet, the lookup tables were generated using parameters values that were estimated from simulations where the model was misspecified in the same way as described for the CNN and ReLERNN above. Sampled chromosomes indicate the number of independent sequences that were sampled from each msprime (Kelleher et al. 2016) coalescent simulation. LDhelmet was not able be used with n = 64 chromosomes and the demographic model could not be intentionally misspecified using FastEPRR.