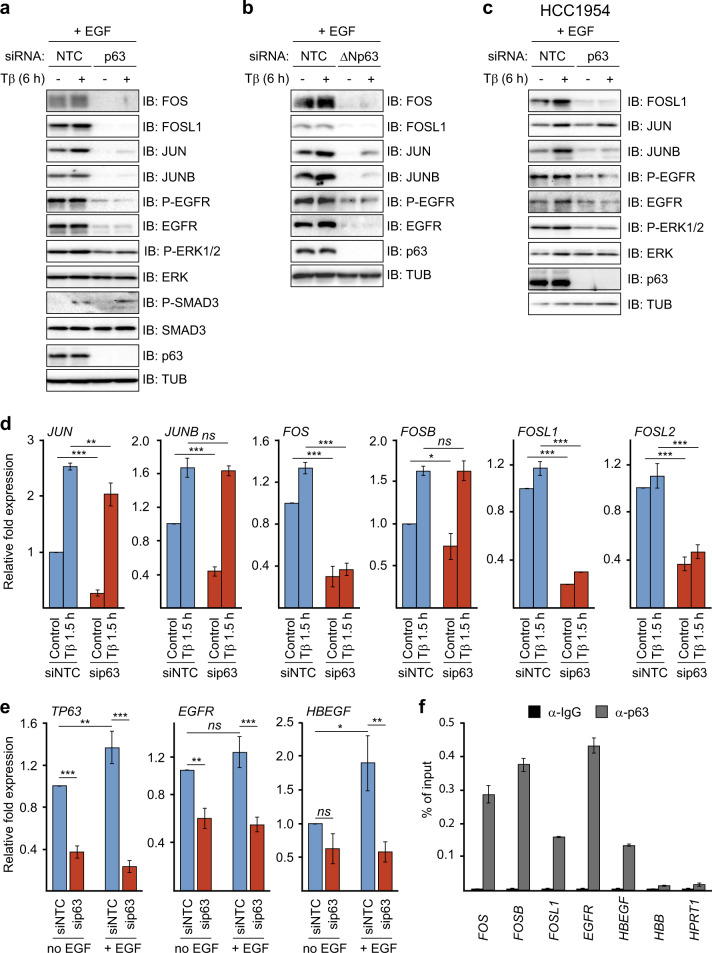
Fig. 5. p63 is essential for JUN/FOS, EGFR and HB-EGF expression.
The effect of p63 knockdown on TGFβ- and EGF-induced AP-1 and EGFR pathway components. MCF10A MII (a, b) and HCC1954 (c) cells were transfected with non-targeting control (siNTC), p63 siRNA, or ΔNp63-specific siRNA, serum-starved for 16 h, stimulated for 6 h with 5 ng/ml TGFβ1 or untreated, and analyzed by immunoblotting. One of three experiments with similar results, is shown. d and e MCF10MII cells were treated as in (a), stimulated with TGFβ1 (5 ng/ml) for 1.5 h (d) or 6 h (e), or untreated, and analyzed by qRT-PCR analysis. Statistics were calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). The data were further analyzed using Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Results from three independent experiments are shown as mean ± SD; ns, not significant, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001. f ChIP-qPCR showing p63 binding to the indicated gene loci in MCF10A MII cells. One of two independent experiments with similar results, is shown.