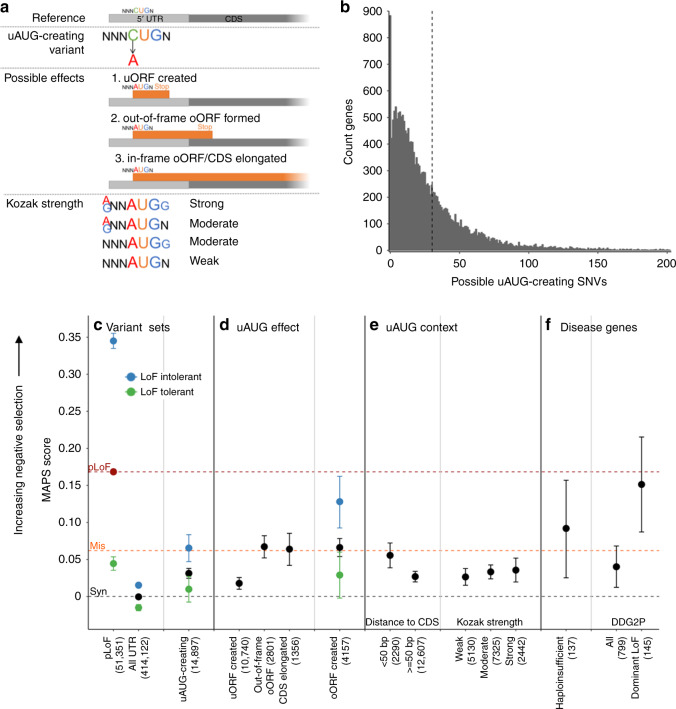
Fig. 1.
uAUG-creating variants have strong signals of negative selection, suggesting they are deleterious. a Schematic of uAUG-creating variants, their possible effects and how the strength of the surrounding Kozak consensus is determined. b The number of possible uAUG-creating SNVs in each of 18,593 genes, truncated at 200 (159 genes have >200). In total we identified 562,196 possible uAUG-creating SNVs, an average of 30.2 per gene (dotted line), with 883 genes having none. c–f MAPS scores (a measure of negative selection) for different variant sets. The number of observed variants for each set is shown in brackets. MAPS for classes of protein-coding SNVs are shown as dotted lines for comparison (synonymous–grey, missense–orange, and predicted loss-of-function (pLoF)–red point and red dotted line). Errors bars were calculated using bootstrapping (see methods). c While overall UTR variants display a selection signature similar to synonymous variants, uAUG-creating variants have significantly higher MAPS (indicative of being more deleterious; permuted P < 1 × 10−4). Variants are further subdivided into those upstream of, or within genes tolerant (green dot) and intolerant (blue dot) to LoF22, with uAUG-creating variants upstream of LoF intolerant genes showing significantly stronger signals of selection than those upstream of LoF tolerant genes (permuted P = 1 × 10−4). pLoF variants are likewise stratified for comparison. d uAUG-creating variants that create an oORF or elongate the CDS show a significantly higher signal of selection than uORF-creating variants (P < 1 × 10−4; oORF created:out-of-frame oORF and CDS elongated combined). e The deleteriousness of uAUG-creating variants depends on the context into which they are created, with stronger selection against uAUG-creation close to the CDS, and with a stronger Kozak consensus sequence. f uAUG-creating variants are under strong negative selection upstream of genes manually curated as haploinsufficient26 and developmental disorder genes reported to act via a dominant LoF mechanism. Abbreviations: CDS coding sequence, uAUG upstream AUG, uORF upstream open reading frame, oORF overlapping open reading frame, MAPS mutability adjusted proportion of singletons, pLoF predicted loss-of-function, DDG2P Developmental Disease Gene to Phenotype