FIGURE 1.
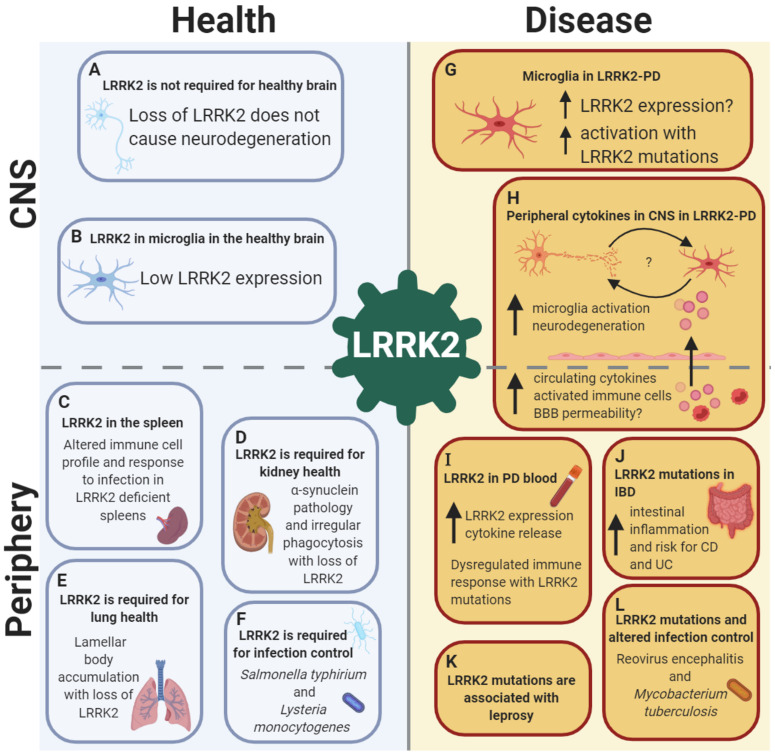
LRRK2 is implicated in health and disease in both the CNS and the periphery, with a crucial role in the immune system. LRRK2 in the healthy brain: (A) LRRK2 may not be essential for neuronal development as global LRRK2 deficiency in rodents is not accompanied by neurodegeneration in dopamine-striatal and other pathways. (B) In the healthy brain, LRRK2 is absent or expressed at low levels in microglia, suggesting a minimal role of LRRK2 in brain-resident innate immune cells under homeostatic conditions. Role of LRRK2 in health in peripheral organs and the immune system: (C) LRRK2 is required for spleen, (D) kidney and (E) lung health, as well as (F) pathogen control and host response to infections such as Salmonella typhirium and Lysteria monocytogenes. LRRK2 in the brain in PD: (G) In LRRK2-PD, LRRK2 expression is increased in microglia, with increased activation of microglia observed with LRRK2-PD mutations. (H) LRRK2 may exert its effects on the brain from the periphery in PD, with increased circulating cytokines potentially increasing BBB permeability with LRRK2 mutations, causing microglia activation and neurodegeneration, leading to bi-directional interplay between neuronal death and microglia priming. Role of LRRK2 in disease in peripheral organs and the immune system: (I) LRRK2 expression is increased in peripheral immune cells in both LRRK2 and non-LRRK2 PD, with concomitant increases in cytokine release. (J) LRRK2 is associated with gut inflammation, with an increased risk of both Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC) with mutations. (K) LRRK2 risk and protective genetic variants are associated with the infectious and autoimmune disease leprosy. (L) LRRK2 mutations have been shown to alter infection control and host response to Reovirus encephalitis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Created with BioRender.com.