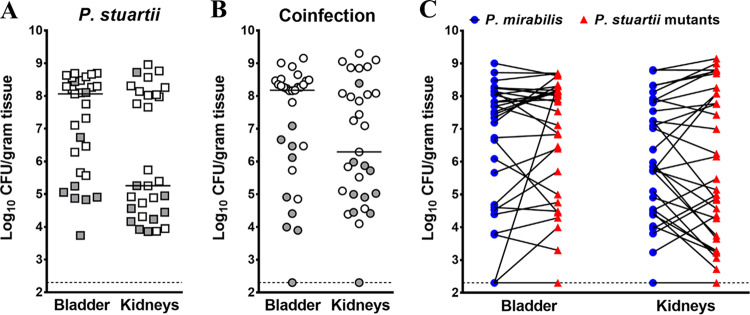
FIG 4.
Colonization by P. stuartii transposon mutants during single-species and polymicrobial CAUTI. For each transposon mutant library pool, 5 to 10 female CBA/J mice were transurethrally inoculated with 1 × 105 CFU of the transposon library for single-species infection (A), and 5 to 10 CBA/J mice were inoculated with 1 × 105 CFU of a 1:1 mixture of the transposon library and wild-type P. mirabilis HI4320 for coinfection (B and C). In all cases, a 4-mm-long segment of catheter tubing was retained in the bladder for the duration of the study. Mice were sacrificed 4 days postinoculation, the bladder and kidneys were homogenized, and an aliquot was plated onto LB agar to determine bacterial burden. The remaining homogenate was fully plated for isolation of bacterial genomic DNA and sequencing. (A and B) Each symbol represents total CFU/gram of tissue from an individual mouse during single-species infection (A) or coinfection (B), and bars indicate the median. Gray-filled symbols indicate mice that were excluded from the study due to low colonization or poor quality of transposon insertion junctions during preparation for sequencing. (C) The majority of coinfected mice were highly colonized by both bacterial species; blue circles represent P. mirabilis CFU/gram of tissue, and red triangles represent P. stuartii CFU/gram of tissue, with values from a single mouse connected by a black line. Dashed lines indicate limit of detection.