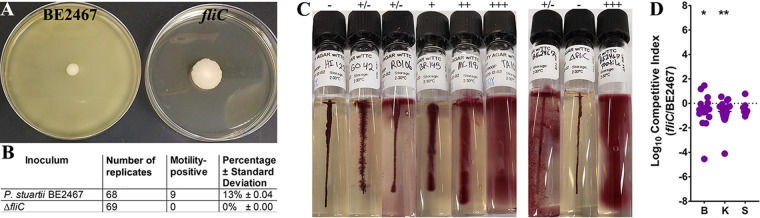
FIG 8.
Flagella contribute to P. stuartii fitness during single-species CAUTI. (A and B) Flagellin-mediated motility was assessed for P. stuartii BE2467 and the isogenic fliC mutant on MOT agar. Both strains were cultured overnight in LB medium and subjected to stab inoculation into 22 to 24 MOT agar plates for each of three independent experiments. Strain BE2467 was found to be predominantly nonmotile in MOT agar, although motility was observed in 13% of replicate plates after 7 days of incubation. In contrast, motility was never detected in the fliC mutant. Panel A shows a representative image of a motile isolate of P. stuartii BE2467 and a typical nonmotile result from the fliC mutant. Panel B shows the combined number of isolates tested and the percentage that exhibited motility. (C) A panel of P. stuartii clinical isolates from the urine of catheterized nursing home residents were assessed for motility using motility test medium with triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) and were compared to P. stuartii BE2467, the fliC mutant, and a motile revertant of BE2467. Images are representative of three independent experiments. Motility scores are indicated as follows: −, no motility; +/−, intermediate motility; +, low motility; ++, moderate motility; +++, high motility. (D) CBA/J mice (n = 20) were transurethrally inoculated with 1 × 105 CFU of a 1:1 mixture of wild-type P. stuartii and the fliC mutant, and a 4-mm segment of catheter tubing was retained in the bladder for the duration of the study. After 96 h, mice were sacrificed and the catheterized bladder (B), kidneys (K), and spleen (S) were homogenized and plated onto LB agar with and without hygromycin to determine bacterial burden of wild-type P. stuartii and the mutant. A competitive index was then calculated on a per-mouse basis using the ratio of mutant to wild-type CFUs in each organ divided by the ratio of mutant to wild-type CFUs from the inoculum (see Materials and Methods). Statistical significance was assessed by Wilcoxon signed-rank test (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01).