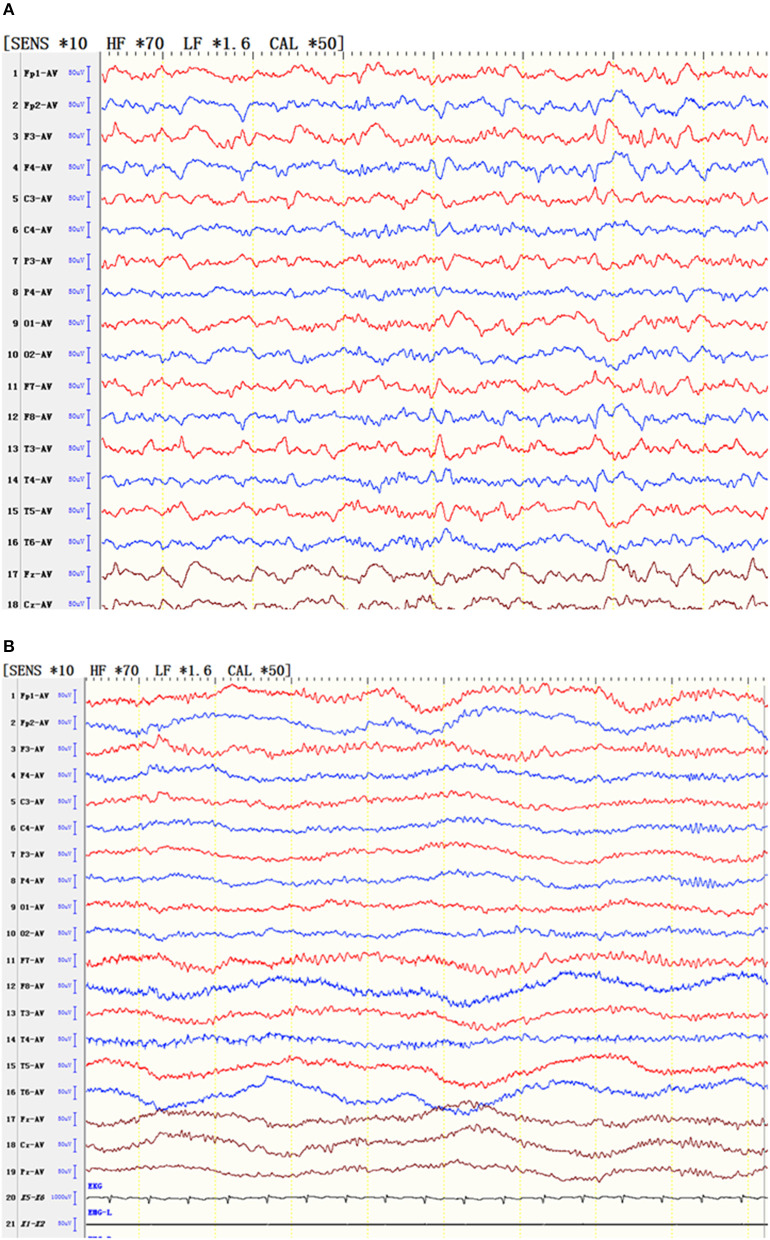
Figure 2.
EEG of a patient with status epilepticus. (A) During the attack, the patient's responses slowed, and the patient gave irrelevant answers. At the same time, the EEG results showed slow waves, sharp waves and fast rhythms in the bilateral frontal and anterior middle temporal areas. (B) After an intravenous injection of diazepam, the patient's consciousness gradually cleared, and the EEG slow wave gradually simultaneously disappeared.