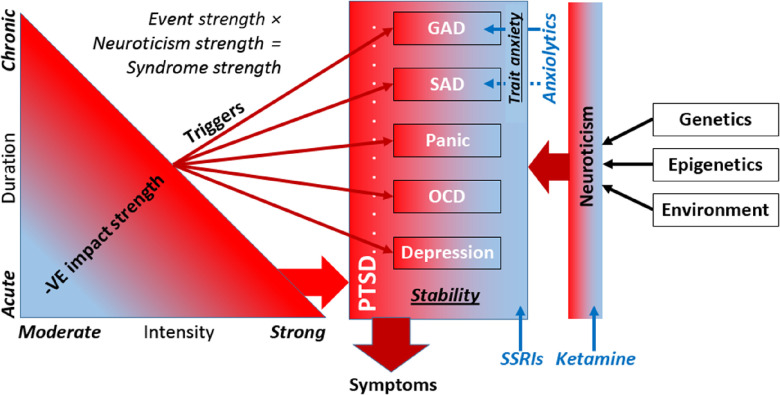
Figure 1.
Diagrammatic representation of the 2-hit hypothesis for disorders known to be affected by ketamine. Disorder is held to result when high neuroticism (resulting from genetic, epigenetic, and prior environmental factors) is combined with a high level of a specific trait linked to GAD, SAD, panic, OCD, or depression. High levels of these specific traits can be triggered by moderate chronic or strong acute stress. In the latter case PTSD may result. Specific anxiolytic drugs affect the specific trait linked to GAD and to a lesser extent SAD (see Table 1). SSRIs act on a background higher order trait of “stability” (DeYoung, 2006), which would not be specific to aversive events (Carver et al., 2008) and which would slowly alter the specific trait levels. Ketamine acts to affect neuroticism and so alters the disordered expression of all the specific traits.