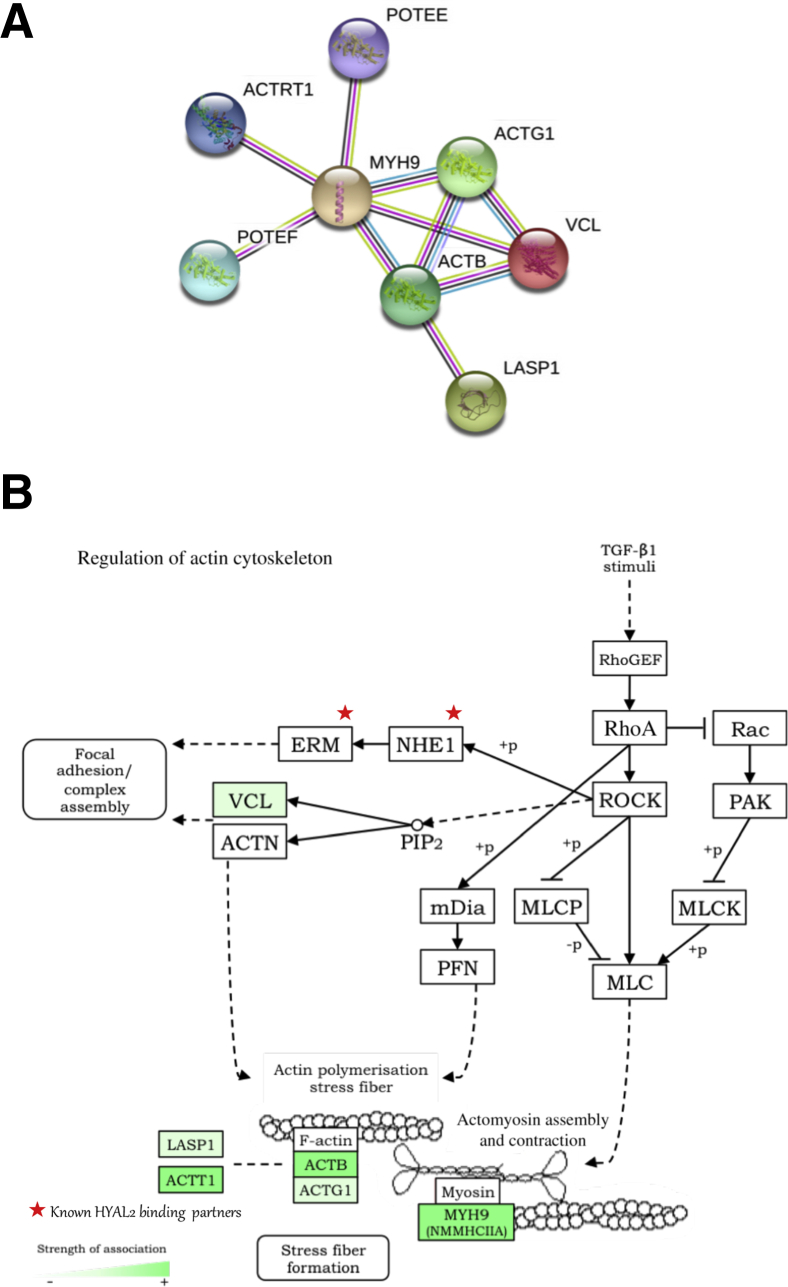
Figure 5.
Proteins co-associated with hyaluronidase (HYAL)-2 have roles in actin organization and contraction function. A: Functional protein–protein association networks of proteins identified from HYAL2 co-immunoprecipitation and mass spectrometry. Protein web was created using the STRING online database version 10.5. B: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) functional pathway of actin cytoskeleton organization. Depth of green indicates strength of HYAL2–protein association, as determined by tandem mass spectrometry peptide identification (where darker green indicates stronger evidence of association). Previously demonstrated HYAL2 associations are highlighted by stars. Pathway map was generated using KEGG Mapper version 2.8 prior to adaption. ACTB, β-actin; ACTG, γ-actin; ACTN, α-actinin; ACTRT1, actin-related protein T1; ACTT, ACT-toxin biosynthesis protein; ETV5, ETS variant transcription factor 5 [also known as Ets-related protein (ERM)]; SLC2A4 regulator, guanine–nucleotide exchange factor (also known as GEF); LASP, LIM and SH3 domain protein; mDia, mammalian diaphanous-related formin; MLC1, modulator of VRAC current 1 [also known as membrane protein (MLC)]; MYLK, myosin light chain kinase (also known as MLCK); MLCP, myosin light-chain phosphatase; MYH9, myosin heavy chain 9 (also known as MNNCHIIA); NHE, Na+/H+ exchanger; PAK, p21-activated kinase; PFN, profilin; PIP, phosphatidylinositol phosphate; POTEE, prostate, ovary, testis-expressed (POTE) ankyrin domain family member E; POTEF, POTE ankyrin domain family member F; ROCK, Rho-associated protein kinase; TGF, transforming growth factor; VCL, vinculin. Panel B adapted with permission from Kanehisa Laboratories.