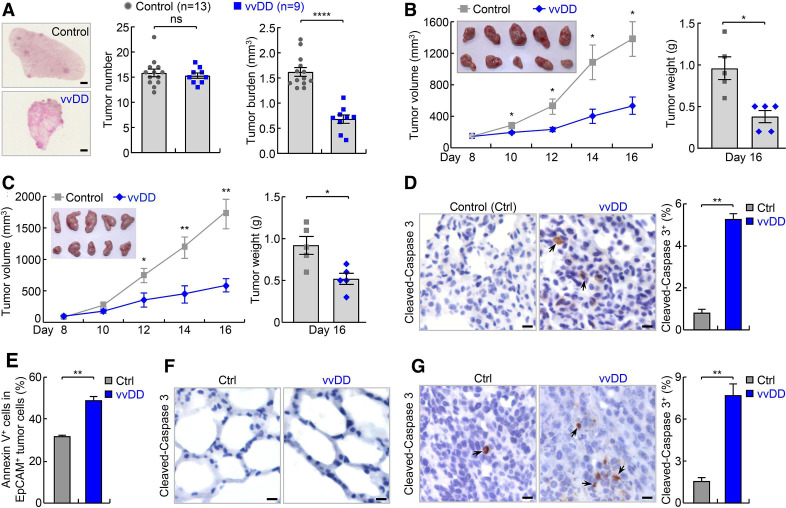
Figure 2.
vvDD shows efficacy in refractory lung cancer in endogenous and syngeneic mouse lung tumor models. (A) Urethane model showing efficacy of vvDD intravenous administration in refractory lung cancer. scale bar, 1 mm. (B) Syngeneic MAD109 lung cancer model showing efficacy of vvDD intratumoral injection in refractory lung cancer (n=5). In tumor image, top row: control; bottom row: vvDD. (C) Syngeneic LAP0297 lung cancer model showing efficacy of vvDD intratumoral injection in refractory lung cancer (n=5). In tumor image, top row: control; bottom row: vvDD. (D–F) IHC and FACS showing increased apoptosis by vvDD treatment in tumor cells ((D), n=9 and (E), n=3), but no obvious apoptosis in normal lung cells (F) in urethane model. Scale bar, 10 µm. (G) IHC showing increased tumor cell apoptosis by vvDD treatment in syngeneic MAD109 model (n=8). Scale bar, 10 µm. FACS, fluorescent activated cell sorting; IHC, immunohistochemistry; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001; ns, not significant; vvDD, vaccinia virus with double deletion.