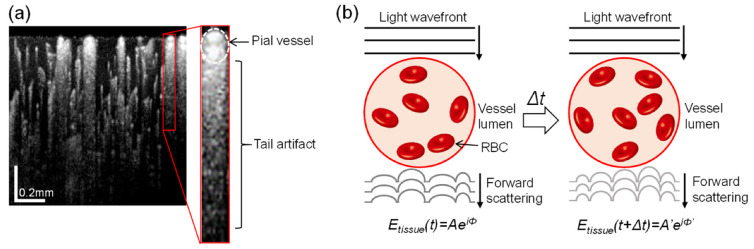
Figure 1.
(a) An example of a log-scaled cross-sectional OCT angiography (OCTA) image of a mouse cerebral cortex. Inset is an enlargement showing a vertical streak (tail) trailing behind a superficial pial vessel. (b) Schematic illustration of the principle behind tail artifacts in OCTA images: changes in the position and density of red blood cells (RBCs) during flow over time causes variance in the forward-scattered wavefront of the light field arriving at the stationary tissue, resulting in spurious graphic artifacts behind the blood vessel during OCTA processing.