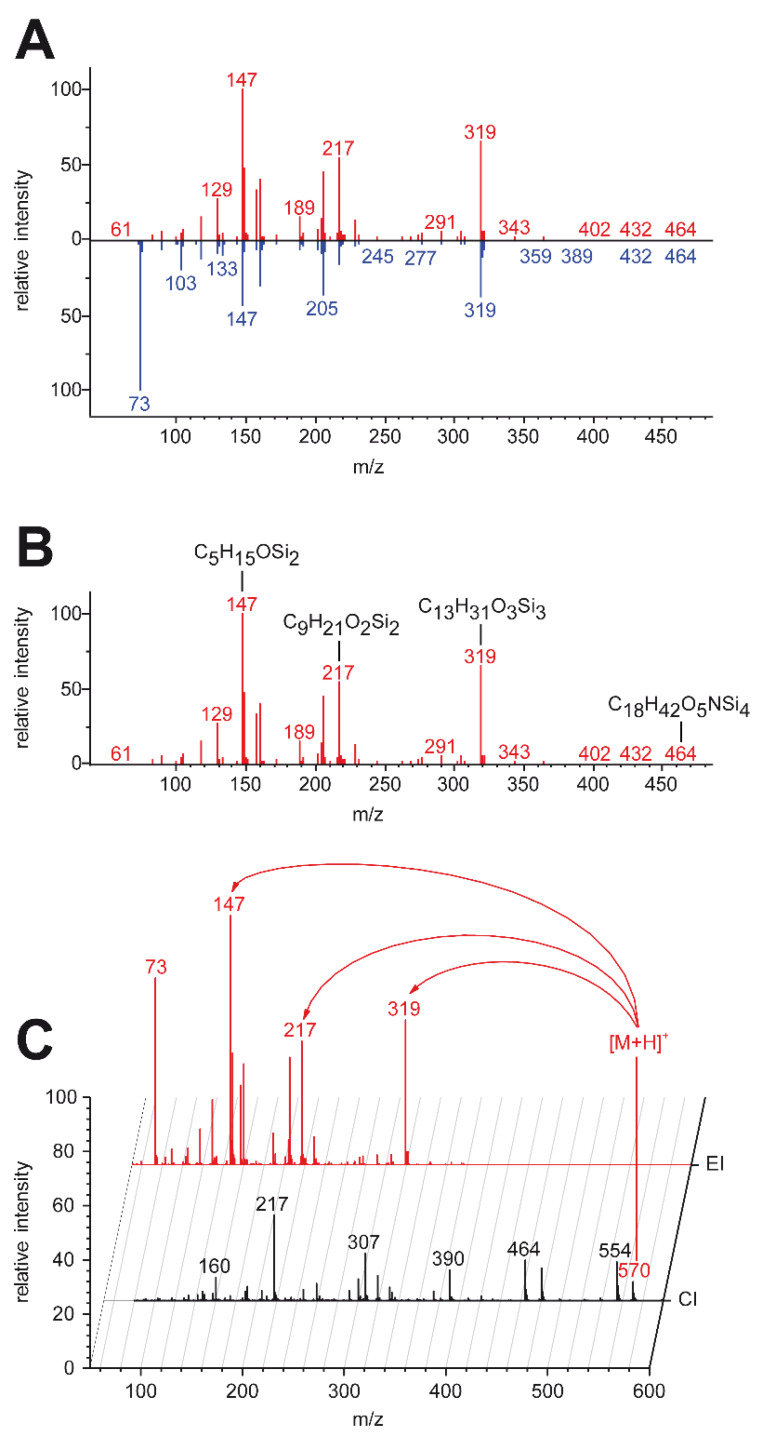
Figure 6.
Metabolite identification workflow using high-resolution GC–MS. (A) EI database matching. Unit-mass EI spectra from commercially and freely available databases (blue) are compared with the unknown spectrum (red). (B) Calculation of sum formulas of several fragments using accurate mass capabilities. If sum formulas fit to the proposed compound by database matching, it is treated as putatively annotated, pending identification by measuring an analytical standard. (C) For unknown compounds with poor database matches, an accurate mass molecular ion from CI measurements (black) is assigned to the EI spectrum of the unknown (red). In silico fragmentation of candidate structures is performed and results are compared with recorded EI data [32].