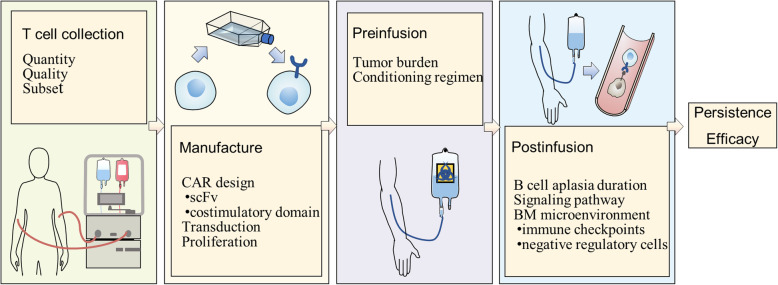
Fig. 1.
Factors influencing CD19 CAR T cell therapy. The limited persistence and impaired efficacy of CAR T cells could be possible mechanisms underlying CD19+ relapse. This figure summarizes potential obstacles to durable remission and better CAR T cell efficacy. First, T cell collection: T cells selected for manufacturing should be of sufficient quantity and good quality and have a phenotype with memory characteristics. Second, CAR T cell manufacture: transgene rejection induced by a murine scFv results in transient in vivo persistence. Selection of the costimulatory domain, transduction technique, especially vector selection, and proliferation method also plays roles in persistence and efficacy. Third, preinfusion: the tumor burden before infusion is associated with patient long-term survival. In addition to lymphodepleting therapy, a conditioning regimen with fludarabine ameliorates T cell persistence. Finally, postinfusion: normal B cells are supposed to recover, but transient B cell aplasia may result in CD19+ relapse. Aberrant signaling pathways and the BM microenvironment will impair a T cell’s potential along with its in vivo persistence