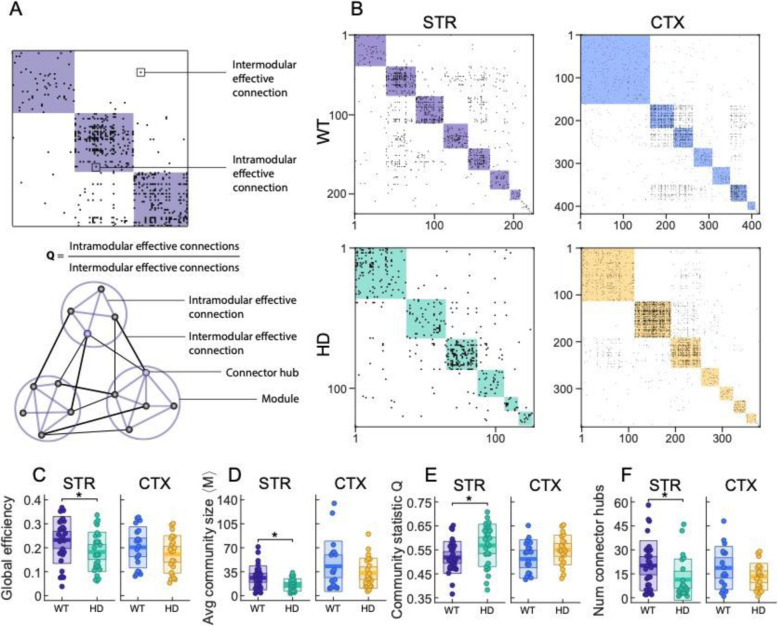
Fig. 2.
Network topology properties of striatal, but not cortical, cultures are altered in HD. a Representative effective connectivity matrix of a neuronal culture. Each dot represents an effective connection from neuron to neuron, i.e., neuron i → neuron j. Communities were identified using the Louvain community detection algorithm and are highlighted in color. Connections between neurons that belong to the same community (module) are intra-modular effective connections, while effective connections between neurons not belonging to the same community are inter-modular connections. b Representative effective connectivity matrices of WT and HD striatal and cortical neuronal cultures. c–f Network topology properties for WT and HD striatal and cortical cultures under basal conditions. c Global efficiency, i.e., average of the inverse shortest path length. d Average community size, i.e., average number of neurons per module. e Community statistic Q. f Average number of connector hubs, i.e., large neuronal nodes that connect mostly with nodes from other communities. Each circle represents a single experiment (STR WT n = 29; STR HD n = 24; CTX WT n = 19; CTX HD n = 22), thick line the mean, thick shaded area the standard error of the mean, and thin shaded area the standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using two-sample Student’s t test between WT and HD populations, *p < 0.05