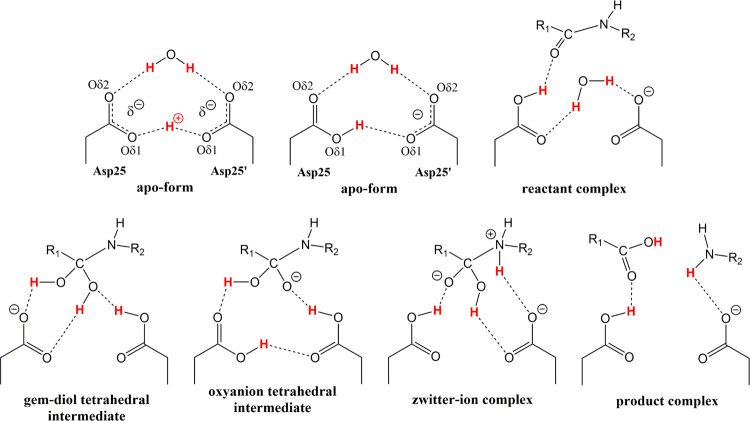
Figure 1.
Chemical diagrams of several possible HIV-1 PR catalytic site structures in the mechanism of peptide bond hydrolysis. H atoms involved in the reaction are colored red, possible hydrogen bond interactions are shown as dashed lines. Catalytic site of the substrate-free (and inhibitor-free) form of enzyme is drawn containing a low-barrier hydrogen bond formed between Oδ1 oxygen atoms of the Asp dyad and with H covalently bound to Asp25 Oδ1. Many other arrangements for the H atom positions in the substrate-free form, reactant and tetrahedral intermediate complexes are also possible.