Figure 4. The AXL and ABL2 tyrosine kinases engage in bidirectional signaling in lung cancer cells.
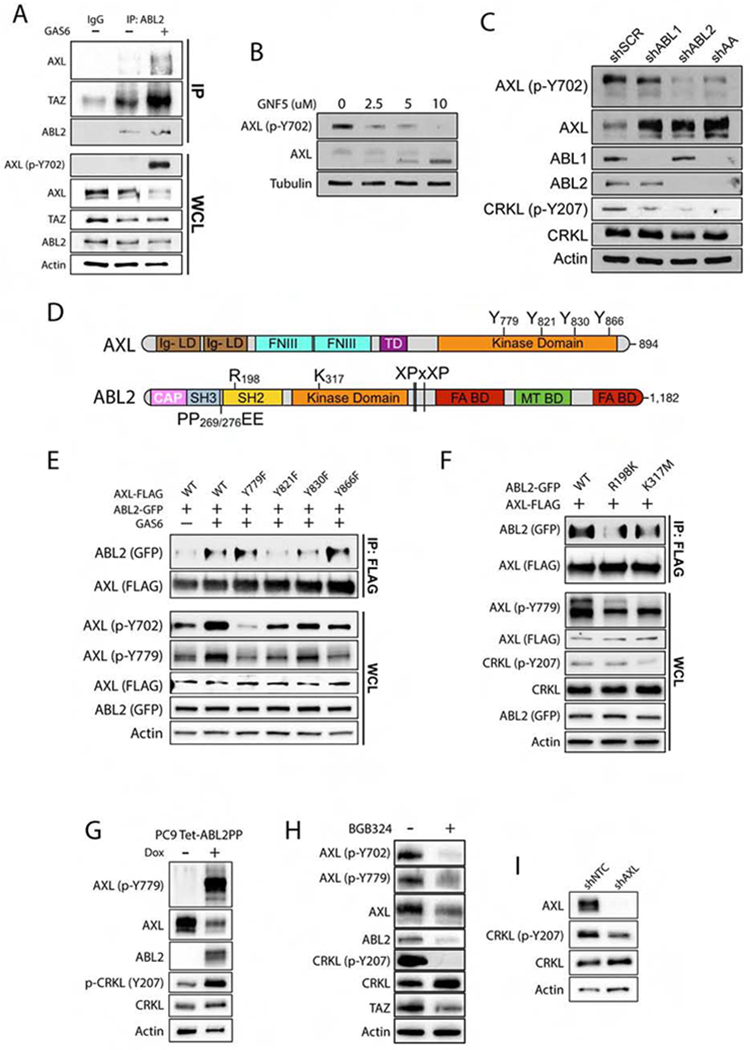
A) Immunoblots of PC9-BrM3 cells treated with 500 ng/mL recombinant human GAS6 for 1 h prior to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-ABL2 antibody (n=3). B) Immunoblots of AXL and p-AXL Y702 in PC9 cells treated with GNF-5 for 24 h. C) Immunoblots of PC9 cells transduced with shRNAs for scramble (SCR), ABL1, ABL2, and ABL1/ABL2 double knockdown (AA) (n=3). D) Schematic of AXL and ABL2 protein structural domains. E) Co-IP of indicated proteins in 293T cells co-transfected with FLAG-AXL WT or phospho-mutants and WT ABL2-GFP plasmids as indicated. Cells were serum-starved for 1 hr prior to addition of 500 ng/mL human GAS6 for 1 h. F) Immunoblots of 293T cells co-transfected with FLAG-AXL and ABL2-GFP wild-type (WT), R198K (SH2-dead) or K317M (kinase dead) mutants. Cells were serum-starved for 1 h prior to treatment with 500 ng/mL GAS6 for 1 h. G) Immunoblot of PC9 cells transduced with inducible active ABL2PP treated with dox for 24 h. H) Immunoblots of PC9-BrM3 cells treated ± 5 uM BGB324 for 24 h. I) Immunoblots of PC9-BrM3 cells transduced with shNTC or shAXL (n=3). WCL: whole cell lysate.
