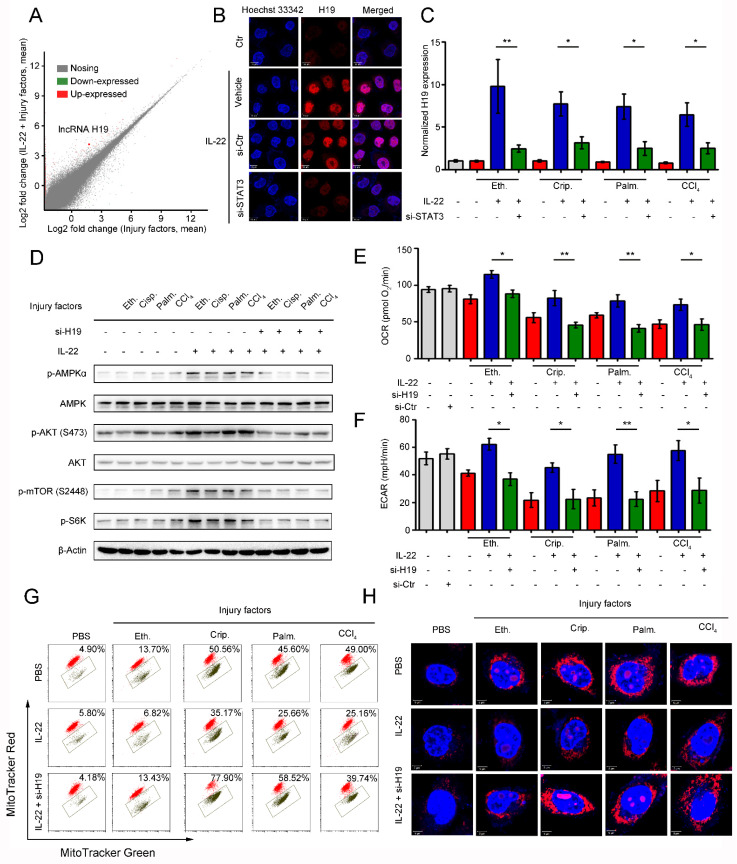
Figure 5.
LncRNA H19 mediates the links between IL-22/IL-22R1 and the AMPK/AKT/mTOR signaling pathways. (A) Bland-Altman plot illustrating relative gene expression in hepatocytes stimulated with or without (control) ethanol, or cisplatin, or palmitic acid, or CCl4 in the absence or presence of IL-22 for the indicated times. (B) Confocal images suggested lncRNA H19 overexpression in hepatocytes after IL-22 treatment, which required STAT3. Control-siRNA (si-Ctr) treated mice as a vehicle control group (n = 5). (C) Real time PCR analysis suggesting that IL-22 induced lncRNA H19 overexpression in hepatocytes, which could be prevented by STAT3 knockdown (n = 3). (D) Comparison of AMPK/AKT/mTOR signaling activation in hepatocytes versus si-H19 treated hepatocytes (lncRNA H19 knockdown). (E and F) Basal OCR and ECAR in hepatocytes at the absence or presence of IL-22, or si-H19 for 24 h (n = 3). (G) Dysfunctional mitochondria were assessed in hepatocytes stained with MitoTracker Green and MitoTracker Red. (H) Confocal images suggested mitochondrial ROS production in hepatocytes stained with MitoSOX. Student's t test (unpaired); *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. All data are means ± SD of at least three independent experiments.